Neuro-Immune Aspects of Schizophrenia with Severe Negative Symptoms: New Diagnostic Markers of Disease Phenotype
- PMID: 35265356
- PMCID: PMC8858398
- DOI: 10.17691/stm2021.13.6.03
Neuro-Immune Aspects of Schizophrenia with Severe Negative Symptoms: New Diagnostic Markers of Disease Phenotype
Abstract
The aim of the study was to analyze the immune-inflammatory profile of patients with paranoid schizophrenia and relate it to the severity of negative symptoms and the MRI data in order to identify biomarkers of schizophrenia severity, search for new approaches to therapy, and control its effectiveness.
Materials and methods: The main group included 51 patients with paranoid schizophrenia, the control group - 30 healthy subjects. Patients underwent MRI scans and immunological studies, which included an assessment of natural and adaptive immunity, the systemic level of key pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and other markers of inflammation.
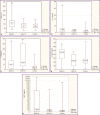
Results: Disorders of immunity and immunoinflammatory profile in patients with paranoid schizophrenia with severe negative symptoms were revealed for the first time: in the presence of severe negative symptoms (>15 points according to the NSA-4 scale), the levels of humoral immunity factors, cytokines IL-10 and IL-12p40 and neurotrophin NGF were increased as well as the markers of systemic inflammation. Morphometric changes in the brain, typical for patients with schizophrenia, and also specific for patients with severe negative symptoms, were determined. The data analysis revealed correlations between the immune changes with structural changes in some of the brain areas, including the frontal cortex and hippocampus. Associations were found between the levels of anti-inflammatory IL-10, IL-12p40 cytokines and morphometric parameters of the brain, specific only for schizophrenic patients with severe negative symptoms.
Conclusion: The interdisciplinary approach, combining brain morphometry with in-depth immunological and clinical studies, made it possible to determine neurobiological, immune, and neurocognitive markers of paranoid schizophrenia with severe negative symptoms. The results are important for further deciphering the pathogenesis of schizophrenia and its subtypes, as well as for the search for new approaches to the treatment of severe forms of the disease.
Keywords: interleukins; neurobiological markers; neurocognitive markers; paranoid schizophrenia; schizophrenia with negative symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest. There are no conflicts of interest associated with this study.
Figures
References
-
- Iasevoli F., Avagliano C., Altavilla B., Barone A., D’Ambrosio L., Matrone M., Notar Francesco D., Razzino E., de Bartolomeis A. Disease. severity in treatment resistant schizophrenia patients is mainly affected by negative symptoms, which mediate the effects of cognitive dysfunctions and neurological soft signs. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:553. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00553.. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corsi-Zuelli F.M.D.G., Brognara F., Quirino G.F.D.S., Hiroki C.H., Fais R.S., Del-Ben C.M., Ulloa L., Salgado H.C., Kanashiro A., Loureiro C.M. Neuroimmune interactions in schizophrenia: focus on vagus nerve stimulation and activation of the alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Front Immunol. 2017;8:618. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00618.. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
