Comparative Genomic Reveals Clonal Heterogeneity in Persistent Staphylococcus aureus Infection
- PMID: 35265532
- PMCID: PMC8900520
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.817841
Comparative Genomic Reveals Clonal Heterogeneity in Persistent Staphylococcus aureus Infection
Abstract
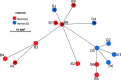
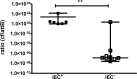
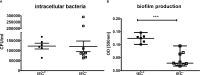
Persistent infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus remain a clinical challenge. Adaptational mechanisms of the pathogen influencing infection persistence, treatment success, and clinical outcome in these types of infections by S. aureus have not been fully elucidated so far. We applied a whole-genome sequencing approach on fifteen isolates retrieved from a persistent S. aureus infection to determine their genetic relatedness, virulome, and resistome. The analysis of the genomic data indicates that all isolates shared a common clonal origin but displayed a heterogenous composition of virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance. This heterogeneity was reflected by different mutations in the rpoB gene that were related to the phenotypic antimicrobial resistance towards rifampicin and different minimal inhibitory concentrations of oxacillin. In addition, one group of isolates had acquired the genes encoding for staphylokinase (sak) and staphylococcal complement inhibitor (scn), leading to the truncation of the hemolysin b (hlb) gene. These features are characteristic for temperate phages of S. aureus that carry genes of the immune evasion cluster and confer triple conversion by integration into the hlb gene. Modulation of immune evasion mechanisms was demonstrated by significant differences in biofilm formation capacity, while invasion and intracellular survival in neutrophils were not uniformly altered by the presence of the immune evasion cluster. Virulence factors carried by temperate phages of S. aureus may contribute to the course of infection at different stages and affect immune evasion and pathogen persistence. In conclusion, the application of comparative genomic demonstrated clonal heterogeneity in persistent S. aureus infection.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; bloodstream infection; comparative genomic; device related infection; immune evasion cluster; phage; sak; scn.
Copyright © 2022 Klein, Morath, Weitz, Schweizer, Sähr, Heeg, Boutin and Nurjadi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis of immune evasion cluster (IEC) genes and intercellular adhesion gene cluster (ICA) among methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive isolates of Staphylococcus aureus.J Prev Med Hyg. 2017 Dec 30;58(4):E308-E314. doi: 10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2017.58.4.711. eCollection 2017 Dec. J Prev Med Hyg. 2017. PMID: 29707662 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of hlb-Converting Bacteriophages in Staphylococcus aureus Host Adaption.Microb Physiol. 2021;31(2):109-122. doi: 10.1159/000516645. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Microb Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34126612 Review.
-
Quadruple or quintuple conversion of hlb, sak, sea (or sep), scn, and chp genes by bacteriophages in non-beta-hemolysin-producing bovine isolates of Staphylococcus aureus.Vet Microbiol. 2007 May 16;122(1-2):190-5. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.01.008. Epub 2007 Jan 17. Vet Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17300883
-
Staphylococcus aureus innate immune evasion is lineage-specific: a bioinfomatics study.Infect Genet Evol. 2013 Oct;19:7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Infect Genet Evol. 2013. PMID: 23792184
-
Temperate Phages of Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Spectr. 2019 Sep;7(5):10.1128/microbiolspec.gpp3-0058-2018. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0058-2018. Microbiol Spectr. 2019. PMID: 31562736 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the translational value of Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) models to determine the risk and severity of Staphylococcal biofilms.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 12:2024.04.29.591689. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.29.591689. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: ACS Infect Dis. 2024 Dec 13;10(12):4156-4166. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00409. PMID: 38746179 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Staphylococcus aureus strains exhibit heterogenous tolerance to direct cold atmospheric plasma therapy.Biofilm. 2023 Apr 15;5:100123. doi: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2023.100123. eCollection 2023 Dec. Biofilm. 2023. PMID: 37138646 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic remodeling by RNA polymerase gene mutations is associated with reduced β-lactam susceptibility in oxacillin-susceptible MRSA.mBio. 2024 Jun 12;15(6):e0033924. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00339-24. Epub 2024 May 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38988221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albano M., Karau M. J., Greenwood-Quaintance K. E., Osmon D. R., Oravec C. P., Berry D. J., et al. . (2019). In Vitro Activity of Rifampin, Rifabutin, Rifapentine, and Rifaximin Against Planktonic and Biofilm States of Staphylococci Isolated From Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63 (11), e00959–19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00959-19 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyle-Vavra S., Jones M., Gourley B. L., Holmes M., Ruf R., Balsam A. R., et al. . (2011). Comparative Genome Sequencing of an Isogenic Pair of USA800 Clinical Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates Obtained Before and After Daptomycin Treatment Failure. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55, 2018–2025. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01593-10 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

