<em>miR-19a</em> targeting <em>CLCA4</em> to regulate the proliferation, migration, and invasion of colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 35266369
- PMCID: PMC8958453
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2022.3381
<em>miR-19a</em> targeting <em>CLCA4</em> to regulate the proliferation, migration, and invasion of colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
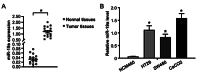
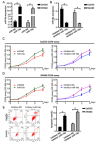
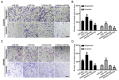
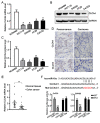
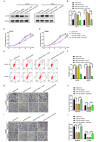
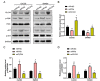
The role of miR-19a in colorectal cancer (CRC), a devastating disease with high mortality and morbidity, remains controversial. In the present study, we show that the level of miR-19a is significantly higher in clinical CRC tissue samples than in paracancerous tissue samples, and significantly higher in CRC cells lines HT29, SW480, and CaCO2 than in the normal human colon mucosal epithelial cell line NCM460. miR-19a mimics and inhibitors were synthesized and validated. Overexpression of miR-19a mimics significantly promoted, while miR-19a inhibitors inhibited, the proliferation, survival, migration, and invasion of SW480 and CaCO2 CRC cells. Furthermore, mRNA and protein levels of chloride channel accessory 4 (CLCA4) were lower in CRC cells and tissues. Bioinformatics and a luciferase reporter assay confirmed that CLCA4 was a miR-19a target. Further, miR-19a inhibition increased CLCA4 expression. The inhibitory effect of miR-19a on cell growth, survival, migration, and invasion was reversed by knockdown of CLCA4 expression. The data demonstrated that the miR-19a/CLCA4 axis modulates phospho-activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in CRC cells. In conclusion, our results revealed that miR-19a overexpression decreases CLCA4 levels to promote CRC oncogenesis, suggesting that miR-19a inhibitors have potential applications for future therapeutic of CRC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calcium-Activated Chloride Channel A4 (CLCA4) Plays Inhibitory Roles in Invasion and Migration Through Suppressing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via PI3K/AKT Signaling in Colorectal Cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Jun 5;25:4176-4185. doi: 10.12659/MSM.914195. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31164625 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of miR-19a partially reversed the resistance of colorectal cancer to oxaliplatin via PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Mar 25;12(7):5640-5650. doi: 10.18632/aging.102929. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32209726 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-410-3p activates the NF-κB pathway by targeting ZCCHC10 to promote migration, invasion and EMT of colorectal cancer.Cytokine. 2021 Apr;140:155433. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155433. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 33517196
-
miR-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1.Mol Cancer. 2017 Mar 4;16(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0625-8. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28257633 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the interaction between miR-19a and CBX7 focusing on the implications for tumor suppression in cancer therapy.Med Oncol. 2023 Dec 19;41(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02251-y. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38112798 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural compounds as regulators of miRNAs: exploring a new avenue for treating colorectal cancer.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Feb 21;25(1):42. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01547-8. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39982533 Review.
-
The multifaceted role of microRNAs in colorectal cancer: pathogenesis and therapeutic implications.Noncoding RNA Res. 2025 May 23;14:65-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2025.05.012. eCollection 2025 Oct. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025. PMID: 40535722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of a new prognostic model for colorectal cancer based on bulk RNA-seq combined with The Cancer Genome Atlas data.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):2704-2720. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-2281. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38988915 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic and metabolic reprogramming in inflammatory bowel diseases: diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Nov 7;23(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03117-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37936149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulated miRNAs Targeting Adiponectin Signaling in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 25;26(15):7196. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157196. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394-424. - PubMed
-
- Center MM, Jemal A, Smith RA, Ward E. Worldwide variations in colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin 2009;59:366-78. - PubMed
-
- Messersmith WA. NCCN guidelines updates: Management of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2019;17:599-601. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

