OPTN/SRTR 2020 Annual Data Report: COVID
- PMID: 35266617
- PMCID: PMC9111379
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16981
OPTN/SRTR 2020 Annual Data Report: COVID
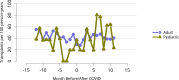
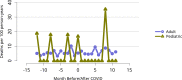
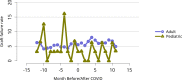
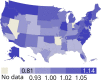
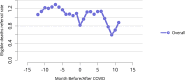
Figures
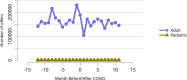

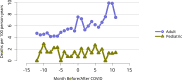
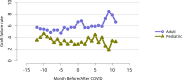
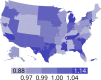
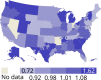
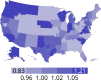
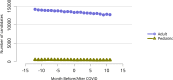
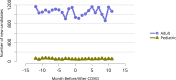
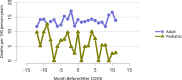
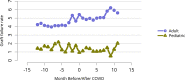
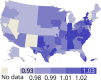
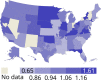

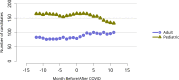
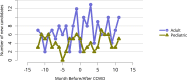

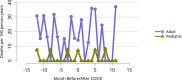
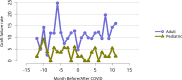
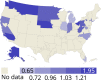
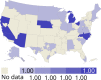

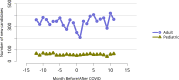
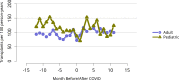
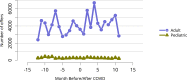
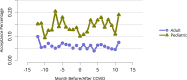
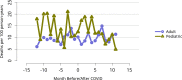
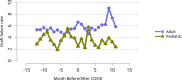
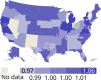
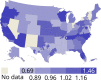
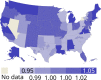
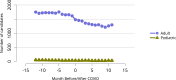
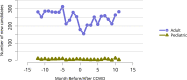
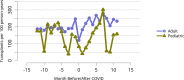
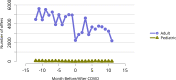
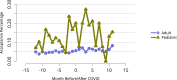

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

