Human safety study of a selective neuronal adenylate cyclase 1 inhibitor NB001 which relieves the neuropathic pain and blocks ACC in adult mice
- PMID: 35266830
- PMCID: PMC9112679
- DOI: 10.1177/17448069221089596
Human safety study of a selective neuronal adenylate cyclase 1 inhibitor NB001 which relieves the neuropathic pain and blocks ACC in adult mice
Abstract
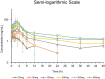
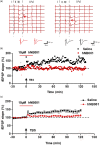
Calcium-dependent, neuronal adenylyl cyclase subtype 1 (AC1) is critical for cortical potentiation and chronic pain. NB001 is a first-in-class drug acting as a selective inhibitor against AC1. The present study delineated the pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of human-used NB001 (hNB001) formulated as immediate-release tablet. This first-in-human (FIH) study was designed as randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. hNB001 showed placebo-like safety and good tolerability in healthy volunteers. A linear dose-exposure relationship was demonstrated at doses between 20 mg and 400 mg. The relatively small systemic exposure of hNB001 in human showed low bioavailability of this compound through oral administration, which can be improved through future dosage research. Food intake had minimal impact on the absorption of hNB001 tablet. Animal experiments further confirmed that hNB001 had strong analgesic effect in animal models of neuropathic pain. In brain slice prepared from the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), bath application of hNB001 blocked the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP). These results from both rodents and human strongly suggest that hNB001 can be safely used for the future treatment of different types of chronic pain in human patients.
Keywords: NB001; anterior cingulate cortex; effectiveness; first-in-human study; pharmacokinetics; safety; tolerability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

