Control over sampling boosts numerical evidence processing in human decisions from experience
- PMID: 35266973
- PMCID: PMC9758588
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhac062
Control over sampling boosts numerical evidence processing in human decisions from experience
Abstract
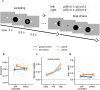
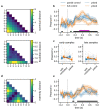
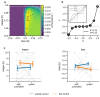
When acquiring information about choice alternatives, decision makers may have varying levels of control over which and how much information they sample before making a choice. How does control over information acquisition affect the quality of sample-based decisions? Here, combining variants of a numerical sampling task with neural recordings, we show that control over when to stop sampling can enhance (i) behavioral choice accuracy, (ii) the build-up of parietal decision signals, and (iii) the encoding of numerical sample information in multivariate electroencephalogram patterns. None of these effects were observed when participants could only control which alternatives to sample, but not when to stop sampling. Furthermore, levels of control had no effect on early sensory signals or on the extent to which sample information leaked from memory. The results indicate that freedom to stop sampling can amplify decisional evidence processing from the outset of information acquisition and lead to more accurate choices.
Keywords: active sampling; decision-making; electroencephalography; information search; number processing.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson NH. Test of a model for number-averaging behavior. Psychon Sci. 1964:1:191–192.
-
- Ansari D, Garcia N, Lucas E, Hamon K, Dhital B. Neural correlates of symbolic number processing in children and adults. Neuroreport. 2005:16:1769–1773. - PubMed
-
- Chambon V, Théro H, Vidal M, Vandendriessche H, Haggard P, Palminteri S. Information about action outcomes differentially affects learning from self-determined versus imposed choices. Nat Hum Behav. 2020:4:1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

