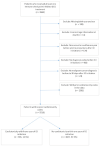
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors-Associated Cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 35267453
- PMCID: PMC8909315
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14051145
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors-Associated Cardiotoxicity
Abstract
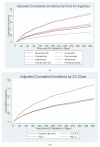
Large population-based studies examining differences in ICI-associated cardiotoxicity across cancer types and agents are limited. Data of 5518 cancer patients who received at least one cycle of ICIs were extracted from a large network of health care organizations. ICI treatment groups were classified by the first ICI agent(s) (ipilimumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, cemiplimab, avelumab, atezolizumab, or durvalumab) or its class (PD-1 inhibitors, PD-L1 inhibitors, CTLA4-inhibitors, or their combination (ipilimumab + nivolumab)). Time to first cardiac adverse event (CAE) (arrhythmia, acute myocardial infarction, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, or pericarditis) developed within one year after ICI initiation was analyzed using a competing-risks regression model adjusting for ICI treatment groups, patient demographic and clinical characteristics, and cancer sites. By month 12, 12.5% developed cardiotoxicity. The most common cardiotoxicity was arrhythmia (9.3%) and 2.1% developed myocarditis. After adjusting for patient characteristics and cancer sites, patients who initiated on monotherapy with ipilimumab (adjusted Hazard Ratio (aHR): 2.00; 95% CI: 1.49−2.70; p < 0.001) or pembrolizumab (aHR: 1.21; 95% CI: 1.01−1.46; p = 0.040) had a higher risk of developing CAEs within one year compared to nivolumab monotherapy. Ipilimumab and pembrolizumab use may increase the risk of cardiotoxicity compared to other agents. Avelumab also estimated a highly elevated risk (aHR: 1.92; 95% CI: 0.85−4.34; p = 0.117) compared to nivolumab and other PD-L1 agents, although the estimate did not reach statistical significance, warranting future studies.
Keywords: cardiac adverse events; cardiotoxicity; immune checkpoint inhibitors; real-world database.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest. C.L. received research funding for an unrelated project sponsored by the University of Utah/AstraZeneca.
Figures

References
-
- Chen R., Zinzani P.L., Fanale M.A., Armand P., Johnson N.A., Brice P., Radford J., Ribrag V., Molin D., Vassilakopoulos T.P., et al. Phase II Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Pembrolizumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2017;35:2125–2132. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.72.1316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

