Pre- and Post-Resection Urine Metabolic Profiles of Bladder Cancer Patients: Results of Preliminary Studies on Time Series Metabolomics Analysis
- PMID: 35267519
- PMCID: PMC8909385
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14051210
Pre- and Post-Resection Urine Metabolic Profiles of Bladder Cancer Patients: Results of Preliminary Studies on Time Series Metabolomics Analysis
Abstract
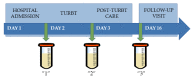
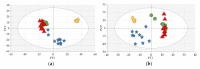
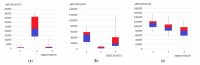
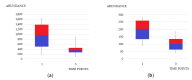
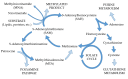
The incidence of bladder cancer (BCa) has remained high for many years. Nevertheless, its pathomechanism has not yet been fully understood and is still being studied. Therefore, multiplatform untargeted urinary metabolomics analysis has been performed in order to study differences in the metabolic profiles of urine samples collected at three time points: before transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT), the day after the procedure and two weeks after TURBT. Collected samples were analyzed with the use of high-performance liquid chromatography hyphenated with time-of-flight mass spectrometry detection (HPLC-TOF/MS) and gas chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry detection (GC-QqQ/MS, in a scan mode). Levels of metabolites selected in our previous study were assessed in order to confirm their potential to differentiate the healthy and diseased samples, regardless of the risk factors and individual characteristics. Hippuric acid, pentanedioic acid and uridine confirmed their potential for sample differentiation. Based on the results of statistical analysis for the paired samples (comparison of metabolic profiles of samples collected before TURBT and two weeks after), a set of metabolites belonging to nucleotide metabolism and methylation processes was also selected. Longitudinal studies proved to be useful for the evaluation of metabolic changes in bladder cancer.
Keywords: TURBT; bladder cancer; metabolic fingerprinting; metabolomics; time series analysis; untargeted metabolomics; urine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The Global Cancer Observatory. [(accessed on 27 October 2021)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/
-
- Ku J.H. Bladder Cancer. Academic Press; London, UK: 2018. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

