Prognostic Impact of High Baseline Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in the Absence of Pathologic Complete Response in Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35267631
- PMCID: PMC8909018
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14051323
Prognostic Impact of High Baseline Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in the Absence of Pathologic Complete Response in Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
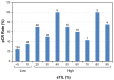
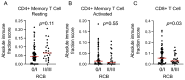
High stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (sTILs) are associated with an improved pathologic complete response (pCR) and survival in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). We hypothesized that high baseline sTILs would have a favorable prognostic impact in TNBC patients without a pCR after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT). In this prospective NACT study, pretreatment biopsies from 318 patients with early-stage TNBC were evaluated for sTILs. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) was applied to search for the sTIL cutoff best associated with a pCR. With ≥20% sTILs identified as the optimal cutoff, 33% patients had high sTILs (pCR rate 64%) and 67% had low sTILs (pCR rate 29%). Patients were stratified according to the sTIL cutoff (low vs. high) and response to NACT (pCR vs. residual disease (RD)). The primary endpoint was event-free survival (EFS), with hazard ratios calculated using the Cox proportional hazards regression model and the 3-year restricted mean survival time (RMST) as primary measures. Within the high-sTIL group, EFS was better in patients with a pCR compared with those with RD (HR 0.05; 95% CI 0.01-0.39; p = 0.004). The difference in the 3-year RMST for EFS between the two groups was 5.6 months (95% CI 2.3-8.8; p = 0.001). However, among patients with RD, EFS was not significantly different between those with high sTILs and those with low sTILs (p = 0.7). RNA-seq analysis predicted more CD8+ T cells in the high-sTIL group with favorable EFS compared with the high-sTIL group with unfavorable EFS. This study did not demonstrate that high baseline sTILs confer a benefit in EFS in the absence of a pCR.
Keywords: CD8; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; pathologic complete response; prognosis; triple-negative breast cancer; tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Herrero-Vicent C., Guerrero A., Gavilá J., Gozalbo F., Hernández A., Sandiego S., Algarra M.A., Calatrava A., Guillem-Porta V., Ruiz-Simón A. Predictive and prognostic impact of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ecancermedicalscience. 2017;11:759. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2017.759. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Denkert C., von Minckwitz G., Darb-Esfahani S., Lederer B., Heppner B.I., Weber K.E., Budczies J., Huober J., Klauschen F., Furlanetto J., et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: A pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:40–50. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30904-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Loi S., Drubay D., Adams S., Pruneri G., Francis P.A., Lacroix-Triki M., Joensuu H., Dieci M.V., Badve S., Demaria S., et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Prognosis: A Pooled Individual Patient Analysis of Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019;37:559–569. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

