The Relationship between Fatty Acids and the Development, Course and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 35268002
- PMCID: PMC8912339
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14051030
The Relationship between Fatty Acids and the Development, Course and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
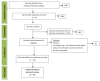
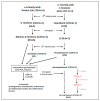
For this systematic review, a search of the relevant literature was conducted in the EMBASE and PubMed databases. We used the following terms: 'rheumatoid arthritis' in conjunction with 'fatty acid'. The following inclusion criteria had to be satisfied for the studies to be included in the analysis: an RCT/observational/cohort study published in English. A total of seventy-one studies were analysed. The presented systematic review of the available data indicates that increased consumption of omega-3 fatty acids (FAs) may have a beneficial effect on human health by decreasing pain and disease activity in patients with RA. The beneficial effect of unsaturated FA on the clinical parameters of RA was demonstrated in all 71 studies analysed. The content of omega-3 FAs in the diet and the consumption of fish, which are their main source, may contribute to a reduced incidence of RA. FAs are an essential component in the synthesis of eicosanoids that exhibit anti-inflammatory properties. Due to the documented positive influence of unsaturated FAs on treatment outcomes, the use of a diet rich in long-chain unsaturated FAs should be the standard of care, along with pharmacotherapy, in the treatment of RA patients. An important element in the control of the treatment process should be the routine assessment of the quality of life of RA patients.
Keywords: fatty acids; nutrition; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gibofsky A. Overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Manag. Care. 2012;18:295–302. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B.A., Bang S.Y., Chowdhury M., Lee H.-S., Kim J.H., Charles P., Venables P., Bae S.-C. Smoking, the HLA-DRB1 shared epitope and ACPA fine-specificity in Koreans with rheumatoid arthritis: Evidence for more than one pathogenic pathway linking smoking to disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014;73:741–747. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202535. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous