Burden of Disease Associated with Dietary Exposure to Aflatoxins in China in 2020
- PMID: 35268003
- PMCID: PMC8912679
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14051027
Burden of Disease Associated with Dietary Exposure to Aflatoxins in China in 2020
Abstract
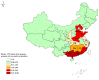
Aflatoxins (AFTs), as a group 1 carcinogen, could lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Dietary intake is the primary way of AFT exposure in humans. However, the contribution of foodborne AFT intake to the HCC burden remains unknown in recent years in China. Hence, the present study was conducted to estimate the burden of HCC attributed to foodborne AFT exposure by using disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). The risk assessment was used to estimate the incidence of HCC related to AFT exposure. Concentrations of AFTs in peanuts, peanut oil, corn, and corn products were retrieved from literature published between 2010 and 2020 in China. Corresponding daily food consumption data were obtained from two nationwide Chinese surveys. A direct approach was used to calculate DALY and DALY rates to quantify the HCC burden attributed to dietary AFT exposure. The total amount of AFT intake through peanut, peanut oil, corn, and corn products was 4.018 ng/kg bw/day resulting in 0.125 extra HCC cases per year/100,000 persons, corresponding to a DALY number and DALY rate of 21,625.08 and 1.53 per 100,000 population, respectively. Regionally, DALYs were high in Guangxi and Guangdong provinces, corresponding to 5948 and 5595 DALYs. A total of 1.5 DALYs/100,000 were lost due to the AFT exposure. DALYs per 100,000 population were higher in several coastal areas. Though the disease burden of HCC caused by dietary AFTs was low in the Chinese population, a high health risk was found in the residents of some areas with high AFT exposure. AFTs are still a health challenge for the Chinese people.
Keywords: aflatoxin; burden of disease; cancer risk; dietary exposure; risk assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical