Body Composition Assessment in Mexican Children and Adolescents. Part 1: Comparisons between Skinfold-Thickness, Dual X-ray Absorptiometry, Air-Displacement Plethysmography, Deuterium Oxide Dilution, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging with the 4-C Model
- PMID: 35268047
- PMCID: PMC8912681
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14051073
Body Composition Assessment in Mexican Children and Adolescents. Part 1: Comparisons between Skinfold-Thickness, Dual X-ray Absorptiometry, Air-Displacement Plethysmography, Deuterium Oxide Dilution, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging with the 4-C Model
Abstract
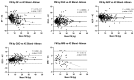
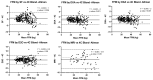
The evaluation of body composition (BC) is relevant in the evaluation of children's health-disease states. Different methods and devices are used to estimate BC. The availability of methods and the clinical condition of the patient usually defines the ideal approach to be used. In this cross-sectional study, we evaluate the accuracy of different methods to estimate BC in Mexican children and adolescents, using the 4-C model as the reference. In a sample of 288 Mexican children and adolescents, 4-C body composition assessment, skinfold-thickness (SF), dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), air displacement plethysmography (ADP), and deuterium dilution (D2O) were performed, along with MRI in a subsample (52 participants). The analysis of validity was performed by correlation analysis, linear regression, and the Bland-Altman method. All methods analyzed showed strong correlations for FM with 4-C values and between each other; however, DXA and MRI overestimated FM, whereas skinfolds and ADP under-estimated FM. Conclusion: The clinical assessment of BC by means of SF, ADP, DXA, MRI and D2O correlated well with the 4-C model and between them, providing evidence of their clinical validity and utility. The results from different methods are not interchangeable. Preference between methods may depend on their availability and the specific clinical setting.
Keywords: MRI 6; air-displacement plethysmography (ADP); body composition; children and adolescents; deuterium dilution; dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA); skinfold-thickness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Air displacement plethysmography, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, and total body water to evaluate body composition in preschool-age children.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012 Dec;112(12):1993-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2012.08.020. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012. PMID: 23174685
-
Comparison of multiple methods to measure maternal fat mass in late gestation.Am J Clin Nutr. 2016 Apr;103(4):1055-63. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.113464. Epub 2016 Feb 17. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26888714 Free PMC article.
-
Air Displacement Plethysmography is an Accurate and Feasible Noninvasive Measure of Fat-Free Mass in Children With Intestinal Failure.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2023 Oct 1;77(4):553-557. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000003883. Epub 2023 Jul 27. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37496142
-
Body composition in preterm infants: a systematic review on measurement methods.Pediatr Res. 2023 Apr;93(5):1120-1140. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02262-x. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 35995939
-
Body-composition assessment via air-displacement plethysmography in adults and children: a review.Am J Clin Nutr. 2002 Mar;75(3):453-67. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/75.3.453. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002. PMID: 11864850 Review.
Cited by
-
Reference ranges for body composition indices by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry from the Bone Mineral Density in Childhood Study Cohort.Am J Clin Nutr. 2023 Oct;118(4):792-803. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.08.006. Epub 2023 Aug 19. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37598746 Free PMC article.
-
Report of a Meeting: An Expert Consultation on Body Composition and Adiposity for Children and Adolescents in All Their Diversity.Curr Dev Nutr. 2025 Jun 3;9(7):107475. doi: 10.1016/j.cdnut.2025.107475. eCollection 2025 Jul. Curr Dev Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40678674 Free PMC article.
-
Reference values for body composition in healthy urban Mexican children and adolescents.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2024 Nov;78(11):979-994. doi: 10.1038/s41430-023-01352-1. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2024. PMID: 37845421 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of anthropometric predictive equations that estimate the total body water and fat-free mass in Tunisian adults.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2023 Apr;77(4):447-453. doi: 10.1038/s41430-023-01262-2. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36726031 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Shamah-Levy T., Vielma-Orozco E., Heredia-Hernández O., Romero-Martínez M., Mojica-Cuevas J., Cuevas-Nasu L., Santaella-Castell J.A., Rivera-Dommarco J. Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición 2018–19: Resultados Nacionales. Instituto Nacional de Salud Pública; Cuernavaca, México: 2020.
-
- INEGI. [(accessed on 10 March 2020)]. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/sistemas/olap/registros/vitales/mortalidad/tabu....
-
- Quetelet A. Sur L’homme et le Développement de ses Facultés. Fayard; Paris, France: 1835.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

