Beneficial Effects of the Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on the Symptoms of Male Accessory Gland Inflammation
- PMID: 35268056
- PMCID: PMC8912840
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14051081
Beneficial Effects of the Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on the Symptoms of Male Accessory Gland Inflammation
Abstract
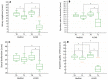
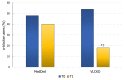
Introduction. Obesity exposes individuals to the risk of chronic inflammation of the prostate gland. Aim and design of the study. A longitudinal clinical study was conducted on selected overweight/obese patients with male accessory gland inflammation (MAGI) to evaluate the effects of body weight loss on their urogenital symptoms. Materials and methods. One hundred patients were selected and assigned to two groups undergoing two different nutritional programs. The first group (n = 50) started a Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) and the second (n = 50) a very-low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD). Before and after three months on the diet, each patient was evaluated for body weight, waist circumference, and MAGI symptoms. The MAGI was assessed using the Structured Interview about MAGI (SI-MAGI), a questionnaire previously designed to assess the symptoms of MAGI. The questionnaire explores four domains, including urinary symptoms, ejaculatory pain or discomfort, sexual dysfunction, and impaired quality of life. Finally, in the two groups, the frequency of an α-blocker used to treat urinary tract symptoms was also evaluated. Results. Patients on MedDiet experienced significant amelioration in urinary symptoms and quality of life. Patients under VLCKD reported not only significant improvement of the same parameters, but also in ejaculatory pain/discomfort and sexual dysfunction. Finally, the percentage of patients on VLCKD taking the α-blocker decreased significantly. Moreover, patients under VLCKD showed a greater loss of body weight than those following the MedDiet. Discussion. The results of this study support the effectiveness of VLCKD in improving the symptoms of patients with MAGI. This improvement involved all of the domains of the SI-MAGI questionnaire and became manifest in a relatively short time. We suggest that a ketogenic nutritional approach can be used in overweight/obese patients with MAGI.
Keywords: MAGI; Mediterranean diet; VLCKD; ejaculatory pain; male accessory gland infection; quality of life; sexual dysfunction; urinary symptoms; very-low-calorie ketogenic diet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of a Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet on Testicular Function in Overweight/Obese Men.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 28;12(10):2967. doi: 10.3390/nu12102967. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32998364 Free PMC article.
-
Chronotype as a predictor of weight loss and body composition improvements in women with overweight or obesity undergoing a very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD).Clin Nutr. 2023 Jul;42(7):1106-1114. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.05.014. Epub 2023 May 19. Clin Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37236871
-
Reduction of Cardio-Metabolic Risk and Body Weight through a Multiphasic Very-Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet Program in Women with Overweight/Obesity: A Study in a Real-World Setting.Nutrients. 2021 May 26;13(6):1804. doi: 10.3390/nu13061804. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34073344 Free PMC article.
-
European Guidelines for Obesity Management in Adults with a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Obes Facts. 2021;14(2):222-245. doi: 10.1159/000515381. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Obes Facts. 2021. PMID: 33882506 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of very low calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) in patients with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2020 Mar;21(1):5-16. doi: 10.1007/s11154-019-09514-y. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2020. PMID: 31705259
Cited by
-
Advancing Obesity Management: the Very Low-Energy Ketogenic therapy (VLEKT) as an Evolution of the "Traditional" Ketogenic Diet.Curr Obes Rep. 2025 Apr 3;14(1):30. doi: 10.1007/s13679-025-00622-2. Curr Obes Rep. 2025. PMID: 40175850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-1202 regulates BPH-1 cell proliferation, apoptosis, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through targeting HMGCL.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 May 25;56(5):675-687. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024001. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38551020 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial for "The Role of Ketogenic Diet in Human Health and Diseases": The Multifaceted Impact of Ketogenic Diets on Health and Disease.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 17;15(18):4027. doi: 10.3390/nu15184027. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764810 Free PMC article.
-
The Ketone Bridge Between the Heart and the Bladder: How Fast Should We Go?Int Neurourol J. 2024 Feb;28(Suppl 1):2-11. doi: 10.5213/inj.2346250.125. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Int Neurourol J. 2024. PMID: 38461852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gacci M., Vignozzi L., Sebastianelli A., Salvi M., Giannessi C., De Nunzio C., Tubaro A., Corona G., Rastrelli G., Santi R., et al. Metabolic syndrome and lower urinary tract symptoms: The role of inflammation. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013;16:101–106. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2012.44. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

