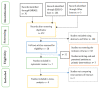
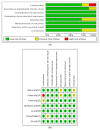
The Effects of Enteral Nutrition in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35268095
- PMCID: PMC8912272
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14051120
The Effects of Enteral Nutrition in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Patients who are critically ill with COVID-19 could have impaired nutrient absorption due to disruption of the normal intestinal mucosa. They are often in a state of high inflammation, increased stress and catabolism as well as a significant increase in energy and protein requirements. Therefore, timely enteral nutrition support and the provision of optimal nutrients are essential in preventing malnutrition in these patients. Aim: This review aims to evaluate the effects of enteral nutrition in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Method: This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted based on the preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-Analysis framework and PICO. Searches were conducted in databases, including EMBASE, Health Research databases and Google Scholar. Searches were conducted from database inception until 3 February 2022. The reference lists of articles were also searched for relevant articles. Results: Seven articles were included in the systematic review, and four articles were included in the meta-analysis. Two distinct areas were identified from the results of the systematic review and meta-analysis: the impact of enteral nutrition and gastrointestinal intolerance associated with enteral nutrition. The impact of enteral nutrition was further sub-divided into early enteral nutrition versus delayed enteral nutrition and enteral nutrition versus parenteral nutrition. The results of the meta-analysis of the effects of enteral nutrition in critically ill patients with COVID-19 showed that, overall, enteral nutrition was effective in significantly reducing the risk of mortality in these patients compared with the control with a risk ratio of 0.89 (95% CI, 0.79, 0.99, p = 0.04). Following sub-group analysis, the early enteral nutrition group also showed a significant reduction in the risk of mortality with a risk ratio of 0.89 (95% CI, 0.79, 1.00, p = 0.05). The Relative Risk Reduction (RRR) of mortality in patients with COVID-19 by early enteral nutrition was 11%. There was a significant reduction in the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score in the early enteral nutrition group compared with the delayed enteral nutrition group. There was no significant difference between enteral nutrition and parenteral nutrition in relation to mortality (RR = 0.87; 95% CI, 0.59, 1.28, p = 0.48). Concerning the length of hospital stay, length of ICU stay and days on mechanical ventilation, while there were reductions in the number of days in the enteral nutrition group compared to the control (delayed enteral nutrition or parenteral nutrition), the differences were not significant (p > 0.05). Conclusion: The results showed that early enteral nutrition significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the risk of mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19. However, early enteral nutrition or enteral nutrition did not significantly (p > 0.05) reduce the length of hospital stay, length of ICU stay and days on mechanical ventilation compared to delayed enteral nutrition or parenteral nutrition. More studies are needed to examine the effect of early enteral nutrition in patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; days on mechanical ventilation; delayed enteral nutrition; early enteral nutrition; enteral nutrition; gastrointestinal intolerance; length of hospital stay; mortality; parenteral nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



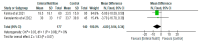
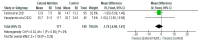

References
-
- Aguila E.J.T., Cua I.H.Y., Fontanilla J.A.C., Yabut V.L.M., Causing M.F.P. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of COVID-19: Impact on Nutrition Practices. Nutrition in Clinical Practice: Official Publication of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020;35:800–805. doi: 10.1002/ncp.10554. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

