Epidural Volume of Injectate Using a Dose Regimen Based on Occipito-Coccygeal Spinal Length (OCL): Randomized Clinical Study Comparing Different Ropivacaine Concentrations, with or without Morphine, in Bitches Undergoing Total Unilateral Mastectomy
- PMID: 35268154
- PMCID: PMC8909377
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12050587
Epidural Volume of Injectate Using a Dose Regimen Based on Occipito-Coccygeal Spinal Length (OCL): Randomized Clinical Study Comparing Different Ropivacaine Concentrations, with or without Morphine, in Bitches Undergoing Total Unilateral Mastectomy
Abstract
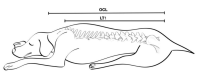
A prospective, randomized clinical trial was designed to compare four epidural treatments in dogs undergoing total unilateral mastectomy. The epidural volume of injectate was based on the individual occipito-coccygeal length (OCL) aiming to reach the first thoracic vertebra (T1). The first ten dogs were allocated in a control group (C) and did not receive epidural treatment. Subsequently, forty dogs were randomly allocated in four groups of ten: epidural ropivacaine 0.5% (R0.5%); morphine 0.1 mg kg−1 plus ropivacaine 0.5% (MR0.5%); morphine 0.1 mg kg−1 plus ropivacaine 0.35% (MR0.35%); morphine 0.1 mg kg−1 plus ropivacaine 0.25% (MR0.25%). Intraoperatively, isoflurane requirement (1.3% vs. <1.1% FE’Iso) and fentanyl requirement (9.8 vs. <1.1 µg kg−1 h−1) were significantly higher in C group compared to all epidural groups. Postoperatively, methadone requirement was higher (1.8 mg kg−1 vs. <0.8 mg kg−1) for C group compared to all epidural treatment groups. The ability to walk and to urinate returned 4 h earlier in MR0.35% and MR0.25%. The mean epidural volume of ropivacaine, using a dose regimen based on OCL, to reach T1 was about 0.15 mL cm−1. The addition of morphine further reduced the methadone requirement, without affecting urinary and motor functions.
Keywords: anaesthesia; dog; epidural; locoregional; mastectomy; morphine; occipito-coccygeal length; ropivacaine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidural administration of combinations of ropivacaine, morphine and xylazine in bitches undergoing total unilateral mastectomy: a randomized clinical trial.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2022 Jan;49(1):126-134. doi: 10.1016/j.vaa.2021.10.001. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2022. PMID: 34742648
-
Preperitoneal ropivacaine infusion versus epidural ropivacaine-morphine for postoperative analgesia in dogs undergoing ovariohysterectomy: a randomized clinical trial.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2021 Nov;48(6):935-942. doi: 10.1016/j.vaa.2021.04.009. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2021. PMID: 34561181
-
Comparison of analgesic efficacy of epidural methadone or ropivacaine/methadone with or without pre-operative oral tepoxalin in dogs undergoing tuberositas tibiae advancement surgery.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2012 Nov;39(6):618-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-2995.2012.00744.x. Epub 2012 Jun 22. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2012. PMID: 22726277 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of opioid-free anaesthesia on postoperative epidural ropivacaine requirement after thoracic surgery: A retrospective unmatched case-control study.Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2019 Oct;38(5):499-505. doi: 10.1016/j.accpm.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2019. PMID: 30731138
-
Thoracic epidural anaesthesia vs intrathecal morphine in dogs undergoing major thoracic and abdominal surgery: clinical study.BMC Vet Res. 2022 May 27;18(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03296-3. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35624498 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Perioperative Pain Management for Mastectomy in Dogs: A Narrative Review.Animals (Basel). 2025 Apr 25;15(9):1214. doi: 10.3390/ani15091214. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40362030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postoperative Analgesic Effect of Bilateral Quadratus Lumborum Block (QLB) for Canine Laparoscopic Ovariectomy: Comparison of Two Concentrations of Ropivacaine.Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 22;13(23):3604. doi: 10.3390/ani13233604. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38066955 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning analysis of factors contributing to hypotension after lumbosacral epidural anaesthesia in dogs undergoing abdominal surgery.Sci Rep. 2025 May 23;15(1):18009. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01991-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40410265 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the Use of Transverse Abdominis Plane Block and Splash Block for Postoperative Pain Control in Dogs Undergoing Mastectomy-A Blinded Randomized Prospective Clinical Study.Animals (Basel). 2025 May 2;15(9):1323. doi: 10.3390/ani15091323. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40362138 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of lumbosacral and sacrococcygeal epidural ropivacaine in dogs undergoing surgery for perineal hernia.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Sep 21;10:1163025. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1163025. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37808102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sorenmo K.U., Worley D.R., Goldschimidt M.H. Tumors of the Mammary Gland. In: Withrow S.J., Vail D.M., Page R.L., editors. Withrow & MacEwen’s Small Animal Clinical Oncology. 5th ed. W.B. Saunders; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2013. pp. 538–556.
-
- Johnston S.A., Tobias K.M. Veterinary Surgery. 2nd ed. Volume 2. Elsevier; Toronto, ON, Canada: 2018. Specific Disorders of the Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue; pp. 1528–1534. Chapter 82.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous