The Coexistence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 35268466
- PMCID: PMC8910939
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11051375
The Coexistence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
The incidence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is growing worldwide. Epidemiological data suggest a strong relationship between NAFLD and T2DM. This is associated with common risk factors and pathogenesis, where obesity, insulin resistance and dyslipidemia play pivotal roles. Expanding knowledge on the coexistence of NAFLD and T2DM could not only protect against liver damage and glucotoxicity, but may also theoretically prevent the subsequent occurrence of other diseases, such as cancer and cardiovascular disorders, as well as influence morbidity and mortality rates. In everyday clinical practice, underestimation of this problem is still observed. NAFLD is not looked for in T2DM patients; on the contrary, diagnosis for glucose metabolism disturbances is usually not performed in patients with NAFLD. However, simple and cost-effective methods of detection of fatty liver in T2DM patients are still needed, especially in outpatient settings. The treatment of NAFLD, especially where it coexists with T2DM, consists mainly of lifestyle modification. It is also suggested that some drugs, including hypoglycemic agents, may be used to treat NAFLD. Therefore, the aim of this review is to detail current knowledge of NAFLD and T2DM comorbidity, its prevalence, common pathogenesis, diagnostic procedures, complications and treatment, with special attention to outpatient clinics.
Keywords: diagnosis; epidemiology; insulin resistance; metabolic syndrome; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; obesity; treatment; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
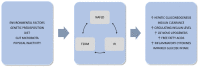
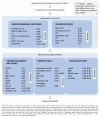
References
-
- Chalasani N., Younossi Z., Lavine J.E., Charlton M., Cusi K., Rinella M., Harrison S.A., Brunt E.M., Sanyal A.J. The Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Practice Guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67:328–357. doi: 10.1002/hep.29367. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

