Different Kinetics of HBV-DNA and HBsAg in HCV Coinfected Patients during DAAs Therapy
- PMID: 35268497
- PMCID: PMC8911219
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11051406
Different Kinetics of HBV-DNA and HBsAg in HCV Coinfected Patients during DAAs Therapy
Abstract
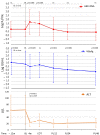
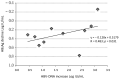
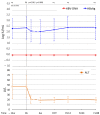
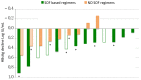
Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) for hepatitis C virus (HCV) may induce hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivations in co-infected patients, whose dynamics and outcomes could depend on the phase of HBV infection. We investigated HBsAg and HBV-DNA kinetics in fifteen untreated HBeAg Negative Infection (ENI) (4F-11M, 62.1y) and eight Nucleos(t)ide Analogs (NAs) treated Chronic Hepatitis B (CHB) (3F-6M, 54.8y) with HCV co-infection, receiving DAAs-regimens including Sofosbuvir (13) or not (10). All achieved a sustained virologic response (SVR) and normalized alanine-aminotransferase (ALT). At the direct acting antivirals’ (DAAs) baseline (BL), the HBV-DNA was undetectable (<6 IU/mL) in eight ENI and all CHB, the mean Log-HBsAg was lower in ENI than CHB (0.88 vs. 2.42, p = 0.035). During DAAs, HBV-DNA increased in untreated ENI by >1 Log in five and became detectable in two. Accordingly, mean BL Log-HBV-DNA (0.89) increased at week-4 (1.78; p = 0.100) and at the end of therapy (1.57; p = 0.104). Mean Log-HBsAg decreased at week-4 in ENI (from 0.88 to 0.55; p = 0.020) and CHB (from 2.42 to 2.15; p = 0.015). After DAAs, the HBsAg returned to pre-treatment levels in CHB, but not in ENI (six cleared HBsAg). Female gender and SOF were associated with a greater HBsAg decline. In conclusion, HBV reactivations during DAAs in HCV co-infected ENI caused moderate increases of HBV-DNA without ALT elevations. The concomitant HBsAg decline, although significant, did not modify individual pre-treatment profiles.
Keywords: HBeAg negative infection; chronic hepatitis B; co-infection; direct acting antivirals; hepatitis B surface antigen; hepatitis B virus; hepatitis C virus; interferon γ-induced protein 10; kinetics; reactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B-related outcomes following direct-acting antiviral therapy in Taiwanese patients with chronic HBV/HCV co-infection.J Hepatol. 2020 Jul;73(1):62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.01.027. Epub 2020 Feb 14. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32061869
-
HBV reactivation in patients with HCV/HBV cirrhosis on treatment with direct-acting antivirals.J Viral Hepat. 2018 Jan;25(1):72-79. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12754. Epub 2017 Aug 9. J Viral Hepat. 2018. PMID: 28703895
-
No evidence of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with resolved infection treated with direct-acting antivirals for hepatitis C in a large real-world cohort.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Aug;46(4):432-439. doi: 10.1111/apt.14177. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28627791
-
Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation Associated With Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C Virus: A Review of Cases Reported to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System.Ann Intern Med. 2017 Jun 6;166(11):792-798. doi: 10.7326/M17-0377. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Ann Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28437794 Review.
-
Progression and status of antiviral monitoring in patients with chronic hepatitis B: From HBsAg to HBV RNA.World J Hepatol. 2018 Sep 27;10(9):603-611. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i9.603. World J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30310538 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Occult HBV Infection in Patients Infected by HIV or HCV: Comparison between HBV-DNA and Two Assays for HBsAg.Viruses. 2024 Mar 7;16(3):412. doi: 10.3390/v16030412. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Global Progress Report on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections. 2021. [(accessed on 28 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240027077.
-
- Wiegand S., Jaroszewicz J., Potthoff A., zu Siederdissen C.H., Maasoumy B., Deterding K., Manns M., Wedemeyer H., Cornberg M. Dominance of hepatitis C virus (HCV) is associated with lower quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen and higher serum interferon-γ-induced protein 10 levels in HBV/HCV-coinfected patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015;21:710.e1–710.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.03.003. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

