The Gut Microbiome, Seleno-Compounds, and Acute Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 35268552
- PMCID: PMC8911090
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11051462
The Gut Microbiome, Seleno-Compounds, and Acute Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
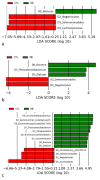
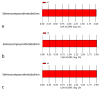
Background: Gut microbiome alterations might be considered a metabolic disorder. However, the relationship between the microbiome and acute myocardial infarction (AMI) has not been properly validated. Methods: The feces of 44 subjects (AMI: 19; control: 25) were collected for fecal genomic DNA extraction. The variable region V3−V4 of the 16S rRNA gene was sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq platform. The metabolite amounts were analyzed using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) metabolic pathways. Results: The bacteria were more enriched in the AMI group both in the observed operational taxonomic units (OTUs) and faith phylogenetic diversity (PD) (p-value = 0.01 and <0.001 with 95% CI, individually). The Selenomonadales were less enriched in the AMI group at the family, genus, and species levels (all linear discriminant analysis (LDA) scores > 2). Seleno-compounds were more abundant in the AMI group at the family, genus, and species levels (all LDA scores > 2). Conclusions: This is the first study to demonstrate the association of Selenomonadales and seleno-compounds with the occurrence of AMI. Our findings provide an opportunity to identify a novel approach to prevent and treat AMI.
Keywords: Selenomonadales; acute coronary syndrome; microbiota; myocardial infarction; seleno-compound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Akbar H., Foth C., Kahloon R.A., Mountfort S. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing LLC.; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2020. Acute Myocardial Infarction ST Elevation (STEMI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

