Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Hemolysis Activities of 10-Hydroxy-2-decenoic Acid against Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 35268586
- PMCID: PMC8912057
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27051485
Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Hemolysis Activities of 10-Hydroxy-2-decenoic Acid against Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
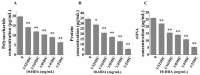
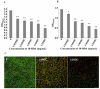
Persistent infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus biofilms pose a major threat to global public health. 10-Hydroxy-2-decenoic acid (10-HDA), a main fatty acid in royal jelly, has been shown to possess various biological activities. The purpose of this study was to explore the effects of 10-HDA on the biofilms and virulence of S. aureus and its potential molecular mechanism. Quantitative crystal violet staining indicated that 10-HDA significantly reduced the biofilm biomass at sub-minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) levels (1/32MIC to 1/2MIC). Scanning electron microscope (SEM) observations demonstrated that 10-HDA inhibited the secretion of extracellular polymeric substances, decreased bacterial adhesion and aggregation, and disrupted biofilm architecture. Moreover, 10-HDA could significantly decrease the biofilm viability and effectively eradicated the mature biofilms. It was also found that the hemolytic activity of S. aureus was significantly inhibited by 10-HDA. qRT-PCR analyses revealed that the expressions of global regulators sarA, agrA, and α-hemolysin gene hla were downregulated by 10-HDA. These results indicate that 10-HDA could be used as a potential natural antimicrobial agent to control the biofilm formation and virulence of S. aureus.
Keywords: 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid; Staphylococcus aureus; biofilm; hemolytic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid of royal jelly exhibits bactericide and anti-inflammatory activity in human colon cancer cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jul 3;18(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2267-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29970062 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin combined with ciprofloxacin and gentamicin inhibits biofilm formation and virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.Microb Pathog. 2025 Mar;200:107297. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2025.107297. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Microb Pathog. 2025. PMID: 39814109
-
Evaluation of anti-biofilm and anti-virulence effect of zinc sulfate on Staphylococcus aureus isolates.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 28;14(1):25747. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75317-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39468094 Free PMC article.
-
Potential antivirulence and antibiofilm activities of sub-MIC of oxacillin against MDR S. aureus isolates: an in-vitro and in-vivo study.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Aug 9;24(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03429-8. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39123138 Free PMC article.
-
Artesunate inhibits Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation by reducing alpha-toxin synthesis.Arch Microbiol. 2021 Mar;203(2):707-717. doi: 10.1007/s00203-020-02077-6. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Arch Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33040179
Cited by
-
Royal Jelly as a Nutraceutical Natural Product with a Focus on Its Antibacterial Activity.Pharmaceutics. 2022 May 27;14(6):1142. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061142. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipids as a key element of insect defense systems.Front Genet. 2023 Jun 9;14:1183659. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1183659. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37359377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Aquatic Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Marine Metagenomes Using a High-Throughput Screening Approach.Mar Drugs. 2025 Apr 20;23(4):178. doi: 10.3390/md23040178. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40278299 Free PMC article.
-
10-Hydroxy-trans-2-decenoic Acid, a New Potential Feed Additive for Broiler Chickens to Improve Growth Performance.Animals (Basel). 2022 Jul 20;12(14):1846. doi: 10.3390/ani12141846. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883394 Free PMC article.
-
Antivirulence activities of retinoic acids against Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 13;14:1224085. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1224085. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37771707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergin S.P., Holland T.L., Fowler V.G., Jr., Tong S.Y.C. Bacteremia, sepsis, and infective endocarditis associated with Staphylococcus aureus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. 2017;409:263–296. - PubMed
-
- Omwenga I., Aboge G.O., Mitema E.S., Obiero G., Ngaywa C., Ngwili N., Wamwere G., Wainaina M., Bett B. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin genes detected in milk from various livestock species in northern pastoral region of Kenya. Food Control. 2019;103:126–132. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.04.005. - DOI
-
- Wu S., Huang J., Wu Q., Zhang J., Zhang F., Yang X., Wu H., Zeng H., Chen M., Ding Y. Staphylococcus aureus isolated from retail meat and meat products in China: Incidence, antibiotic resistance and genetic diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2018;9:2767. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02767. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

