Plant-Derived Molecule 4-Methylumbelliferone Suppresses FcεRI-Mediated Mast Cell Activation and Allergic Inflammation
- PMID: 35268679
- PMCID: PMC8912031
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27051577
Plant-Derived Molecule 4-Methylumbelliferone Suppresses FcεRI-Mediated Mast Cell Activation and Allergic Inflammation
Abstract
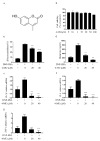
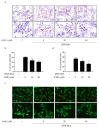
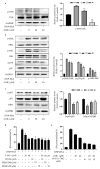
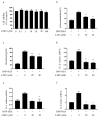
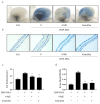
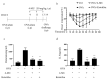
Mast cells (MCs) are an important treatment target for high-affinity IgE Fc receptor (FcεRI)-mediated allergic diseases. The plant-derived molecule 4-methylumbelliferone (4-MU) has beneficial effects in animal models of inflammation and autoimmunity diseases. The aim of this study was to examine 4-MU effects on MC activation and probe the underlying molecular mechanism(s). We sensitized rat basophilic leukemia cells (RBLs) and mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) with anti-dinitrophenol (DNP) immunoglobulin (Ig)E antibodies, stimulated them with exposure to DNP-human serum albumin (HSA), and then treated stimulated cells with 4-MU. Signaling-protein expression was determined by immunoblotting. In vivo allergic responses were examined in IgE-mediated passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA) and ovalbumin (OVA)-induced active systemic anaphylaxis (ASA) mouse models. 4-MU inhibited β-hexosaminidase activity and histamine release dose-dependently in FcεRI-activated RBLs and BMMCs. Additionally, 4-MU reduced cytomorphological elongation and F-actin reorganization while down-regulating IgE/Ag-induced phosphorylation of SYK, NF-κB p65, ERK1/2, p38, and JNK. Moreover, 4-MU attenuated the PCA allergic reaction (i.e., less ear thickening and dye extravasation). Similarly, we found that 4-MU decreased body temperature, serum histamine, and IL4 secretion in OVA-challenged ASA model mice. In conclusion, 4-MU had a suppressing effect on MC activation both in vitro and in vivo and thus may represent a new strategy for treating IgE-mediated allergic conditions.
Keywords: 4-methylumbelliferone; FcεRI signaling; SYK; mast cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resveratrol inhibits IgE-mediated basophilic mast cell degranulation and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in mice.J Nutr. 2013 May;143(5):632-9. doi: 10.3945/jn.112.173302. Epub 2013 Mar 20. J Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23514766
-
Flavoring agent dihydrocoumarin alleviates IgE-mediated mast cell activation and allergic inflammation.Food Funct. 2022 Mar 21;13(6):3621-3631. doi: 10.1039/d2fo00190j. Food Funct. 2022. PMID: 35262138
-
Leaves and pseudostems extract of Curcuma longa attenuates immunoglobulin E/bovine serum albumin-stimulated bone marrow-derived cultured mast cell activation and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in BALB/c mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 1;321:117529. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117529. Epub 2023 Nov 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38042384
-
Human IgE-independent systemic anaphylaxis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Jun;137(6):1674-1680. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.02.015. Epub 2016 Apr 26. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27130857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role Played by Autophagy in FcεRI-Dependent Activation of Mast Cells.Cells. 2024 Apr 16;13(8):690. doi: 10.3390/cells13080690. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38667305 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Formononetin Inhibits Mast Cell Degranulation to Ameliorate Compound 48/80-Induced Pseudoallergic Reactions.Molecules. 2023 Jul 7;28(13):5271. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135271. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446928 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effects of Grewia tomentosa Juss. on IgE-Mediated Allergic Reaction and DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis.Plants (Basel). 2022 Sep 27;11(19):2540. doi: 10.3390/plants11192540. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36235405 Free PMC article.
-
4-methylumbilliferon (4-MU) as a Potential Treatment Against Cerebral ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Rats; An Experimental Study.Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2024 Sep 17;13(1):e8. doi: 10.22037/aaem.v13i1.2456. eCollection 2025. Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39465056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin F., Li X., Deng Y., Timilshina M., Huang B., Kim D.Y., Chang J.H., Ichinose H., Baek S.H., Murakami M., et al. The orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 promotes FcepsilonRI-stimulated mast cell activation and anaphylaxis by counteracting the inhibitory LKB1/AMPK axis. Allergy. 2019;74:1145–1156. doi: 10.1111/all.13702. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

