Sustainable Valorization of Tomato By-Products to Obtain Bioactive Compounds: Their Potential in Inflammation and Cancer Management
- PMID: 35268802
- PMCID: PMC8911995
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27051701
Sustainable Valorization of Tomato By-Products to Obtain Bioactive Compounds: Their Potential in Inflammation and Cancer Management
Abstract
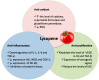
Tomato producing and processing industries present undoubted potential for industrial discarded products valorization whether due to the overproduction of fresh tomatoes or to the loss during processing. Although tomato by-products are not yet considered a raw material, several studies have suggested innovative and profitable applications. It is often referred to as "tomato pomace" and is quite rich in a variety of bioactive compounds. Lycopene, vitamin C, β-carotene, phenolic compounds, and tocopherol are some of the bioactives herein discussed. Tomato by-products are also rich in minerals. Many of these compounds are powerful antioxidants with anti-inflammatory properties besides modulating the immune system. Several researchers have focused on the possible application of natural ingredients, especially those extracted from foods, and their physiological and pharmacological effects. Herein, the effects of processing and further applications of the bioactive compounds present in tomato by-products were carefully reviewed, especially regarding the anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects. The aim of this review was thus to highlight the existing opportunities to create profitable and innovative applications for tomato by-products in health context.
Keywords: anti-cancer; anti-inflammatory; oleoresins; peel; pomace; seeds; tomato; tomato processing industry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tomato|Description, Cultivation, & History|Britannica. [(accessed on 5 March 2020)]. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/plant/tomato.
-
- Perveen R., Suleria H.A.R., Anjum F.M., Butt M.S., Pasha I., Ahmad S. Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum) Carotenoids and Lycopenes Chemistry; Metabolism, Absorption, Nutrition, and Allied Health Claims—A Comprehensive Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015;55:919–929. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.657809. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kumar S., Meena M., Meena D., Meena J.K., Kishor S., Kishor S., Kishor S. Performance of Tomato Germplasms for Growth, Yield and Quality under Lucknow Conditions. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017;6:1560–1562.
-
- FAOSTAT Production Quantities (Crops) of Tomatoes, World + (Total) [(accessed on 25 March 2020)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC.
-
- FAOSTAT Production Quantities of Tomatoes by Country (Average-1994–2018) [(accessed on 31 October 2020)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC/visualize.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

