(-)-Naringenin 4',7-dimethyl Ether Isolated from Nardostachys jatamansi Relieves Pain through Inhibition of Multiple Channels
- PMID: 35268839
- PMCID: PMC8911579
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27051735
(-)-Naringenin 4',7-dimethyl Ether Isolated from Nardostachys jatamansi Relieves Pain through Inhibition of Multiple Channels
Abstract
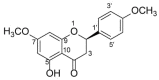
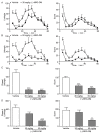
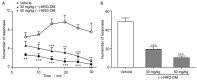
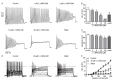
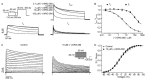
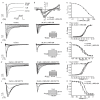
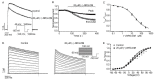
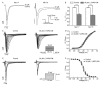
(-)-Naringenin 4',7-dimethyl ether ((-)-NRG-DM) was isolated for the first time by our lab from Nardostachys jatamansi DC, a traditional medicinal plant frequently used to attenuate pain in Asia. As a natural derivative of analgesic, the current study was designed to test the potential analgesic activity of (-)-NRG-DM and its implicated mechanism. The analgesic activity of (-)-NRG-DM was assessed in a formalin-induced mouse inflammatory pain model and mustard oil-induced mouse colorectal pain model, in which the mice were intraperitoneally administrated with vehicle or (-)-NRG-DM (30 or 50 mg/kg) (n = 10 for each group). Our data showed that (-)-NRG-DM can dose dependently (30~50 mg/kg) relieve the pain behaviors. Notably, (-)-NRG-DM did not affect motor coordination in mice evaluated by the rotarod test, in which the animals were intraperitoneally injected with vehicle or (-)-NRG-DM (100, 200, or 400 mg/kg) (n = 10 for each group). In acutely isolated mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons, (-)-NRG-DM (1~30 μM) potently dampened the stimulated firing, reduced the action potential threshold and amplitude. In addition, the neuronal delayed rectifier potassium currents (IK) and voltage-gated sodium currents (INa) were significantly suppressed. Consistently, (-)-NRG-DM dramatically inhibited heterologously expressed Kv2.1 and Nav1.8 channels which represent the major components of the endogenous IK and INa. A pharmacokinetic study revealed the plasma concentration of (-)-NRG-DM is around 7 µM, which was higher than the effective concentrations for the IK and INa. Taken together, our study showed that (-)-NRG-DM is a potential analgesic candidate with inhibition of multiple neuronal channels (mediating IK and INa).
Keywords: (−)-Naringenin 4′,7-dimethyl ether; analgesic candidate; delayed rectifier potassium currents; ion channels; mechanism study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel isoquinoline alkaloid HJ-69 isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum attenuates inflammatory pain by inhibiting voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Aug 10;330:118218. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118218. Epub 2024 Apr 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38677570
-
Effects of Sesamin, the Major Furofuran Lignan of Sesame Oil, on the Amplitude and Gating of Voltage-Gated Na+ and K+ Currents.Molecules. 2020 Jul 4;25(13):3062. doi: 10.3390/molecules25133062. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32635522 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanolic extract of Aconiti Brachypodi Radix attenuates nociceptive pain probably via inhibition of voltage-dependent Na⁺ channel.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012 Jul 1;9(4):574-83. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v9i4.15. eCollection 2012. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012. PMID: 23983394 Free PMC article.
-
The Natural Flavonoid Naringenin Elicits Analgesia through Inhibition of NaV1.8 Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019 Dec 18;10(12):4834-4846. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00547. Epub 2019 Nov 21. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31697467
-
A review of nardosinone for pharmacological activities.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 5;908:174343. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174343. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34265296 Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoids as Modulators of Potassium Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 9;24(2):1311. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021311. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids: A treasure house of prospective pharmacological potentials.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 9;10(6):e27533. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27533. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38496846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological Evaluation of the Anesthetic and Analgesic Potential of Injection Harsha 22: A Novel Polyherbal Local Anesthetic Formulation Intended for Parenteral Administration in Wistar Albino Rats.J Exp Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 27;15:149-161. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S402277. eCollection 2023. J Exp Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37008368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Okifuji A., Skinner M. Chapter 70—Psychological Aspects of Pain. Curr. Ther. Pain. 2009;24:513–518.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81825021/National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars
- 81773707, 32161143019/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020284/Youth Innovation Promotion Association
- 19431906000/Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality
- 20JR5RA570/Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

