Nucleic Acid-Based Nanobiosensor (NAB) Used for Salmonella Detection in Foods: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35269310
- PMCID: PMC8912873
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12050821
Nucleic Acid-Based Nanobiosensor (NAB) Used for Salmonella Detection in Foods: A Systematic Review
Abstract
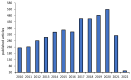
Salmonella bacteria is a foodborne pathogen found mainly in food products causing severe symptoms in the individual, such as diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps after consuming the infected food, which can be fatal in some severe cases. Rapid and selective methods to detect Salmonella bacteria can prevent outbreaks when ingesting contaminated food. Nanobiosensors are a highly sensitive, simple, faster, and lower cost method for the rapid detection of Salmonella, an alternative to conventional enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques. This study systematically searched and analyzed literature data related to nucleic acid-based nanobiosensors (NABs) with nanomaterials to detect Salmonella in food, retrieved from three databases, published between 2010 and 2021. We extracted data and critically analyzed the effect of nanomaterial functionalized with aptamer or DNA at the limit of detection (LOD). Among the nanomaterials, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were the most used nanomaterial in studies due to their unique optical properties of the metal, followed by magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) of Fe3O4, copper nanoparticles (CuNPs), and also hybrid nanomaterials multiwalled carbon nanotubes (c-MWCNT/AuNP), QD/UCNP-MB (quantum dotes upconverting nanoparticle of magnetic beads), and cadmium telluride quantum dots (CdTe QDs@MNPs) showed excellent LOD values. The transducers used for detection also varied from electrochemical, fluorescent, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), RAMAN spectroscopy, and mainly colorimetric due to the possibility of visualizing the detection result with the naked eye. Furthermore, we show the magnetic separation system capable of detecting the target amplification of the genetic material. Finally, we present perspectives, future research, and opportunities to use point-of-care (POC) diagnostic devices as a faster and lower cost approach for detecting Salmonella in food as they prove to be viable for resource-constrained environments such as field-based or economically limited conditions.
Keywords: aptamer; bacteria detection; biosensor; magnetic system; nanomaterials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Simultaneous Colorimetric Detection of a Variety of Salmonella spp. in Food and Environmental Samples by Optical Biosensing Using Oligonucleotide-Gold Nanoparticles.Front Microbiol. 2019 May 31;10:1138. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01138. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31214132 Free PMC article.
-
A Microfluidic Biosensor Based on Magnetic Nanoparticle Separation, Quantum Dots Labeling and MnO2 Nanoflower Amplification for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Mar 9;11(3):281. doi: 10.3390/mi11030281. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32182880 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobiosensors for revolutionizing parasitic infections diagnosis: a critical review to improve global health with an update on future challenges prospect.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jun 16;30(1):484. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02685-2. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40524269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamer-based fluorometric determination of Salmonella Typhimurium using Fe3O4 magnetic separation and CdTe quantum dots.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 19;14(6):e0218325. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218325. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31216306 Free PMC article.
-
Gold-based hybrid nanomaterials for biosensing and molecular diagnostic applications.Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Jun 15;80:543-559. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.02.015. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016. PMID: 26894985 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment of a Simple, Sensitive, and Specific Salmonella Detection Method Based on Recombinase-Aided Amplification Combined with dsDNA-Specific Nucleases.Foods. 2024 Apr 29;13(9):1380. doi: 10.3390/foods13091380. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38731750 Free PMC article.
-
Gold Nanoparticles in Nanobiotechnology: From Synthesis to Biosensing Applications.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 5;9(28):29966-29982. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c10352. eCollection 2024 Jul 16. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39035946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles in Biomedical Sciences: Properties, Current Trends, Novel Opportunities and Emerging Challenges in Theranostic Nanomedicine.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;13(3):424. doi: 10.3390/nano13030424. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36770385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Biosensors for Pesticide Detection in Foods.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 27;12(8):572. doi: 10.3390/bios12080572. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36004968 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Applications of Nanobiosensors in Pathogen Detection in Water and Food.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Oct 11;13(10):922. doi: 10.3390/bios13100922. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887115 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ma X., Xu X., Xia Y., Wang Z. SERS aptasensor for Salmonella typhimurium detection based on spiny gold nanoparticles. Food Control. 2018;84:232–237. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.07.016. - DOI
-
- Ye Y., Yan W., Liu Y., He S., Cao X., Xu X., Zheng H., Gunasekaran S. Electrochemical detection of Salmonella using an invA genosensor on polypyrrole-reduced graphene oxide modified glassy carbon electrode and AuNPs-horseradish peroxidase-streptavidin as nanotag. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2019;1074:80–88. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.05.012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- [E-26/203.049/2017] [E-26/010.000.984/2019]; [E-E26/203.187/2019]; [E-26/201.167/2020]/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- [313119/2020-1]; [150450/2020-6]/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- [88887.518753/2020-00]/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

