Cerebral Biomarkers and Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity in Preeclampsia
- PMID: 35269411
- PMCID: PMC8909006
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11050789
Cerebral Biomarkers and Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity in Preeclampsia
Abstract
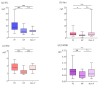
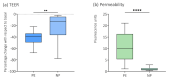
Cerebral complications in preeclampsia contribute substantially to maternal mortality and morbidity. There is a lack of reliable and accessible predictors for preeclampsia-related cerebral complications. In this study, plasma from women with preeclampsia (n = 28), women with normal pregnancies (n = 28) and non-pregnant women (n = 16) was analyzed for concentrations of the cerebral biomarkers neurofilament light (NfL), tau, neuron-specific enolase (NSE) and S100B. Then, an in vitro blood−brain barrier (BBB) model, based on the human cerebral microvascular endothelial cell line (hCMEC/D3), was employed to assess the effect of plasma from the three study groups. Transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) was used as an estimation of BBB integrity. NfL and tau are proteins expressed in axons, NSE in neurons and S100B in glial cells and are used as biomarkers for neurological injury in other diseases such as dementia, traumatic brain injury and hypoxic brain injury. Plasma concentrations of NfL, tau, NSE and S100B were all higher in women with preeclampsia compared with women with normal pregnancies (8.85 vs. 5.25 ng/L, p < 0.001; 2.90 vs. 2.40 ng/L, p < 0.05; 3.50 vs. 2.37 µg/L, p < 0.001 and 0.08 vs. 0.05 µg/L, p < 0.01, respectively). Plasma concentrations of NfL were also higher in women with preeclampsia compared with non-pregnant women (p < 0.001). Higher plasma concentrations of the cerebral biomarker NfL were associated with decreased TEER (p = 0.002) in an in vitro model of the BBB, a finding which indicates that NfL could be a promising biomarker for BBB alterations in preeclampsia.
Keywords: NSE; NfL; S100B; blood-brain barrier; cerebral biomarkers; in vitro studies; preeclampsia; pregnancy; tau.
Conflict of interest statement
H.Z. has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Alector, Eisai, Denali, Roche, Wave, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Pinteon Therapeutics, Nervgen, AZTherapies, CogRx and Red Abbey Labs, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure and Biogen, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Blood-based cerebral biomarkers in preeclampsia: Plasma concentrations of NfL, tau, S100B and NSE during pregnancy in women who later develop preeclampsia - A nested case control study.PLoS One. 2018 May 2;13(5):e0196025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196025. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29719006 Free PMC article.
-
Signs of neuroaxonal injury in preeclampsia-A case control study.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 8;16(2):e0246786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246786. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33556141 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cerebral Biomarkers in Women With Preeclampsia Are Still Elevated 1 Year Postpartum.Am J Hypertens. 2016 Dec 1;29(12):1374-1379. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpw097. Am J Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27653032
-
Review: The potential role of placental extracellular vesicles in blood-brain barrier disruption and neuroinflammation in preeclampsia.Placenta. 2025 Apr 10:S0143-4004(25)00104-3. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2025.04.001. Online ahead of print. Placenta. 2025. PMID: 40229181 Review.
-
Septic encephalopathy in the elderly - biomarkers of potential clinical utility.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Sep 7;17:1238149. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1238149. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37744876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cis P-tau is a central circulating and placental etiologic driver and therapeutic target of preeclampsia.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 5;14(1):5414. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41144-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37669931 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Role of Pin1-Cis P-Tau-ApoE Axis in the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia and Its Connection with Dementia.Biomedicines. 2024 Dec 26;13(1):29. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010029. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39857613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preeclampsia history and postpartum risk of cerebrovascular disease and cognitive impairment: Potential mechanisms.Front Physiol. 2023 Mar 31;14:1141002. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1141002. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37064920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Utility of Maternal Blood S100B in Women with Suspected or Established Preeclampsia-A Systematic Review.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 8;15(6):840. doi: 10.3390/biom15060840. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563479 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the Pin1-cis P-tau axis in the development and treatment of vascular contribution to cognitive impairment and dementia and preeclampsia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Apr 2;12:1343962. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1343962. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38628595 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tranquilli A.L., Dekker G., Magee L., Roberts J., Sibai B.M., Steyn W., Zeeman G.G., Brown M.A. The classification, diagnosis and management of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: A revised statement from the ISSHP. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2014;4:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2014.02.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brown M.A., Magee L.A., Kenny L.C., Karumanchi S.A., McCarthy F.P., Saito S., Hall D.R., Warren C.E., Adoyi G., Ishaku S., et al. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: ISSHP Classification, Diagnosis, and Management Recommendations for International Practice. Hypertension. 2018;72:24–43. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10803. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

