Revealing the Roles of MOAP1 in Diseases: A Review
- PMID: 35269511
- PMCID: PMC8909730
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11050889
Revealing the Roles of MOAP1 in Diseases: A Review
Abstract
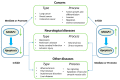
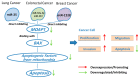
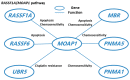
Modulator of apoptosis protein1 (MOAP1), also known as MAP1 and PNMA4, belongs to the PNMA gene family consisting of at least 15 genes located on different chromosomes. MOAP1 interacts with the BAX protein, one of the most important apoptosis regulators. Due to its critical role in a few of disease-associated pathways, MOAP1 is associated with many diseases such as cancers and neurological diseases. In this study, we introduced MOAP1 and its biological functions and reviewed the associations between MOAP1 and a few diseases including cancers, neurological diseases, and other diseases such as inflammation and heart diseases. We also explained possible biological mechanisms underlying the associations between MOAP1 and these diseases, and discussed a few future directions regarding MOAP1, especially its potential roles in neurodegenerative disorders. In summary, MOAP1 plays a critical role in the development and progression of cancers and neurological diseases by regulating a few genes related to cellular apoptosis such as BAX and RASSF1A and interacting with disease-associated miRNAs, including miR-25 and miR1228.
Keywords: MOAP1; apoptosis; biomarker; cancer; neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-1228 prevents cellular apoptosis through targeting of MOAP1 protein.Apoptosis. 2012 Jul;17(7):717-24. doi: 10.1007/s10495-012-0710-9. Apoptosis. 2012. PMID: 22434376
-
Human Cytomegalovirus miR-UL70-3p Downregulates the H2O2-Induced Apoptosis by Targeting the Modulator of Apoptosis-1 (MOAP1).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 21;23(1):18. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010018. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008453 Free PMC article.
-
The BAX-binding protein MOAP1 associates with LC3 and promotes closure of the phagophore.Autophagy. 2021 Nov;17(11):3725-3739. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1896157. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33783314 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on Livin protein: an inhibitor of apoptosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Nov;357(1-2):39-45. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0873-7. Epub 2011 May 27. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21617971 Review.
-
MicroRNA and cancer--focus on apoptosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Jan;13(1):12-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00510.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19175697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional control of motor pool formation and motor circuit connectivity by the LIM-HD protein Isl2.Elife. 2023 Oct 23;12:e84596. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84596. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37869988 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Machine Learning Methods Reveal Key Biomarkers of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 13;13:927545. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.927545. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35910196 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant RDH12-retinitis pigmentosa impairs photoreceptor development and implicates cone involvement in retinal organoids.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Apr 29;13:1511066. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1511066. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40365019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hertz C.E., Bayarri-Olmos R., Kirketerp-Moller N., van Putten S., Pilely K., Skjoedt M.O., Garred P. Chimeric Proteins Containing MAP-1 and Functional Domains of C4b-Binding Protein Reveal Strong Complement Inhibitory Capacities. Front. Immunol. 2018;9:1945. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01945. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials