Waste Clearance in the Brain and Neuroinflammation: A Novel Perspective on Biomarker and Drug Target Discovery in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 35269541
- PMCID: PMC8909773
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11050919
Waste Clearance in the Brain and Neuroinflammation: A Novel Perspective on Biomarker and Drug Target Discovery in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
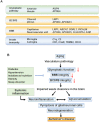
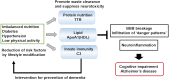
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a multifactorial disease with a heterogeneous etiology. The pathology of Alzheimer's disease is characterized by amyloid-beta and hyperphosphorylated tau, which are necessary for disease progression. Many clinical trials on disease-modifying drugs for AD have failed to indicate their clinical benefits. Recent advances in fundamental research have indicated that neuroinflammation plays an important pathological role in AD. Damage- and pathogen-associated molecular patterns in the brain induce neuroinflammation and inflammasome activation, causing caspase-1-dependent glial and neuronal cell death. These waste products in the brain are eliminated by the glymphatic system via perivascular spaces, the blood-brain barrier, and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Age-related vascular dysfunction is associated with an impairment of clearance and barrier functions, leading to neuroinflammation. The proteins involved in waste clearance in the brain and peripheral circulation may be potential biomarkers and drug targets in the early stages of cognitive impairment. This short review focuses on waste clearance dysfunction in AD pathobiology and discusses the improvement of waste clearance as an early intervention in prodromal AD and preclinical stages of dementia.
Keywords: Aβ clearance; blood-brain barrier; glymphatic system; innate immunity; mild cognitive impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
The author is a board member and shareholder of MCBI, Inc. (Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan).
Figures

References
-
- Gauthier S., Rosa-Neto P., Morais J.A., Webster C. World Alzheimer Report 2021: Journey through the Diagnosis of Dementia. Alzheimer’s Disease International; London, UK: 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

