Tracking the Molecular Fingerprint of Head and Neck Cancer for Recurrence Detection in Liquid Biopsies
- PMID: 35269544
- PMCID: PMC8910330
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23052403
Tracking the Molecular Fingerprint of Head and Neck Cancer for Recurrence Detection in Liquid Biopsies
Abstract
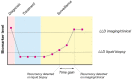
The 5-year relative survival for patients with head and neck cancer, the seventh most common form of cancer worldwide, was reported as 67% in developed countries in the second decade of the new millennium. Although surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or combined treatment often elicits an initial satisfactory response, relapses are frequently observed within two years. Current surveillance methods, including clinical exams and imaging evaluations, have not unambiguously demonstrated a survival benefit, most probably due to a lack of sensitivity in detecting very early recurrence. Recently, liquid biopsy monitoring of the molecular fingerprint of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma has been proposed and investigated as a strategy for longitudinal patient care. These innovative methods offer rapid, safe, and highly informative genetic analysis that can identify small tumors not yet visible by advanced imaging techniques, thus potentially shortening the time to treatment and improving survival outcomes. In this review, we provide insights into the available evidence that the molecular tumor fingerprint can be used in the surveillance of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Challenges to overcome, prior to clinical implementation, are also discussed.
Keywords: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; liquid biopsy; minimal residual disease; relapse; surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

