Interleukin-1 Induces the Release of Lubricating Phospholipids from Human Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes
- PMID: 35269552
- PMCID: PMC8910712
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23052409
Interleukin-1 Induces the Release of Lubricating Phospholipids from Human Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes
Abstract
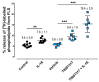
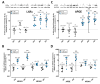
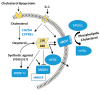
(1) Background: Synovial fluid (SF) from knee joints with osteoarthritis (OA) has increased levels of phospholipids (PL). We have reported earlier that TGF-ß and IGF-1 stimulate fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) to synthesize increased amounts of PLs. The current study examined whether IL-1ß induces the release of PLs in FLS and the underlying mechanism. (2) Methods: Cultured human OA FLS were treated with IL-1ß alone and with pathway inhibitors or with synthetic liver X receptor (LXR) agonists. Cholesterol hydroxylases, ABC transporters, apolipoproteins (APO), LXR, sterol regulatory binding proteins (SREBPs), and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR) were analyzed by RT-PCR, Western blot, and ELISA. The release of radiolabeled PLs from FLS was determined, and statistical analysis was performed using R (N = 5-9). (3) Results: Like synthetic LXR agonists, IL-1ß induced a 1.4-fold greater release of PLs from FLS. Simultaneously, IL-1ß upregulated the level of the PL transporter ABCA1 and of cholesterol hydroxylases CH25H and CYP7B1. IL-1ß and T0901317 stimulated the expression of SREBP1c, whereas only T0901317 enhanced SREBP2, HMGCR, APOE, LXRα, and ABCG1 additionally. (4) Conclusions: IL-1ß partially controls PL levels in OA-SF by affecting the release of PLs from FLS. Our data show that IL-1ß upregulates cholesterol hydroxylases and thus the formation of oxysterols, which, as natural agonists of LXR, increase the level of active ABCA1, in turn enhancing the release of PLs.
Keywords: ABCA1; CH25H; CYP7B1; FLS; LXR; cholesterol hydroxylase; interleukin; osteoarthritis; phospholipids; synovial fibroblasts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Cao Y., Kampf N., Kosinska M.K., Steinmeyer J., Klein J. Interactions between Bilayers of Phospholipids Extracted from Human Osteoarthritic Synovial Fluid. Biotribology. 2021;25:100157. doi: 10.1016/j.biotri.2020.100157. - DOI
-
- Kosinska M.K., Ludwig T.E., Liebisch G., Zhang R., Siebert H.-C., Wilhelm J., Kaesser U., Dettmeyer R.B., Klein H., Ishaque B., et al. Articular Joint Lubricants during Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Display Altered Levels and Molecular Species. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0125192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125192. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

