Methyl Donors Reduce Cell Proliferation by Diminishing Erk-Signaling and NFkB Levels, While Increasing E-Cadherin Expression in Panc-1 Cell Line
- PMID: 35269689
- PMCID: PMC8910410
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23052546
Methyl Donors Reduce Cell Proliferation by Diminishing Erk-Signaling and NFkB Levels, While Increasing E-Cadherin Expression in Panc-1 Cell Line
Abstract
Pancreatic cancer is an aggressive malignancy with high metastatic potential. There are several lifestyle-related determinants in its etiology, including diet. Methyl donors are dietary micronutrients which play an important role in fueling vital metabolic pathways, and as bioactive food components provide methyl groups as substrates and cofactors. The imbalanced nutritional status of methyl donors has recently been linked to pathological conditions. Therefore, we hypothesized that dietary methyl donors may improve the physiology of cancer patients, including those with pancreatic cancer, and could be used for intervention therapy. In this study, methyl-donor treatment (L-methionine, choline chloride, folic acid and vitamin B12) of an aggressive pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line (Panc-1) resulted in significantly increased p21WAF1/Cip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor levels, along with apoptotic SubG1 fractions. At the same time, phospho-Erk1/2 levels and proliferation rate were significantly reduced. Though methyl-donor treatments also increased the pro-apoptotic protein Bak, Puma and Caspase-9, it failed to elevate cleaved Caspase-3 levels. In addition, the treatment significantly reduced the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-17a and the transcription factor NFkB. Similarly, a significant decrease in VEGF and SDF-1a levels were detected, which may indicate reduced metastatic potential. As expected, E-cadherin expression was inversely associated with these changes, showing elevated expression after methyl-donor treatment. In summary, we found that methyl donors may have the potential to reduce aggressive and proliferative phenotype of Panc-1 cells. This suggests a promising role of dietary methyl donors for complementing relevant cancer therapies, even in treatment-resistant pancreatic adenocarcinomas.
Keywords: E-cadherin; apoptosis; cell cycle; methyl donors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



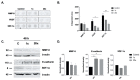
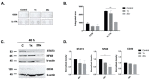

Similar articles
-
Methyl-Donors Can Induce Apoptosis and Attenuate Both the Akt and the Erk1/2 Mediated Proliferation Pathways in Breast and Lung Cancer Cell Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 30;22(7):3598. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073598. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808426 Free PMC article.
-
Novel signaling molecules implicated in tumor-associated fatty acid synthase-dependent breast cancer cell proliferation and survival: Role of exogenous dietary fatty acids, p53-p21WAF1/CIP1, ERK1/2 MAPK, p27KIP1, BRCA1, and NF-kappaB.Int J Oncol. 2004 Mar;24(3):591-608. Int J Oncol. 2004. PMID: 14767544
-
Alisertib induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy and suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition involving PI3K/Akt/mTOR and sirtuin 1-mediated signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancer cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jan 17;9:575-601. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S75221. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25632225 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of p21WAF1/CIP1, p27Kip1, p53 and E-cadherin expression in gastric cancer.J Clin Pathol. 2007 Jul;60(7):756-61. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2006.038976. Epub 2007 May 4. J Clin Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17483253 Free PMC article.
-
New possible silver lining for pancreatic cancer therapy: Hydrogen sulfide and its donors.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 May;11(5):1148-1157. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.019. Epub 2020 Oct 31. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34094825 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Dietary Methyl-Donor Intake and Other Lifestyle Factors on Cancer Patients in Hungary.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 13;14(18):4432. doi: 10.3390/cancers14184432. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139592 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Edible Medicinal Mushrooms and Their Potential Use as Therapeutic Agents Against Insulin Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 19;26(2):827. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020827. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859540 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

