A Core Set of Snap Bean Genotypes Established by Phenotyping a Large Panel Collected in Europe
- PMID: 35270047
- PMCID: PMC8912712
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11050577
A Core Set of Snap Bean Genotypes Established by Phenotyping a Large Panel Collected in Europe
Abstract
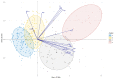
Snap beans are a group of bean cultivars grown for their edible immature pods. The objective of this work was to characterize the diversity of pod phenotypes in a snap bean panel (SBP), comprising 311 lines collected in Europe, and establish a core set (Core-SBP) with the maximum diversity of pod phenotypes. Phenotyping of the SBP was carried out over two seasons based on 14 quantitative pod dimension traits along with three qualitative traits: pod color, seed coat color, and growth habit. Phenotypes were grouped into 54 classes using a hierarchical method, and a Core-SBP with one line per phenotype class was established. A further field-based evaluation of the Core-SBP revealed higher diversity index values than those obtained for the SBP. The Core-SBP was also genotyped using 24 breeder-friendly DNA markers tagging 21 genomic regions previously associated with pod trait control. Significant marker-trait associations were found for 11 of the 21 analyzed regions as well as the locus fin. The established Core-SBP was a first attempt to classify snap bean cultivars based on pod morphology and constituted a valuable source of characteristics for future breeding programs and genetic analysis.
Keywords: Phaseolus vulgaris L.; QTL validation; core collections; diversity; genotyping; phenotyping; pod traits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Van Schoonhoven A., Pastor Corrales M.A., editors. Standard System for the Evaluation of Bean Germplasm. Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT); Cali, Colombia: 1987. p. 53.
-
- Chaurasia S. Green beans. In: Jaiswal A.K., editor. Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Fruits and Vegetables. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2020. pp. 289–300. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

