The Effect of Problematic Social Media Use on Happiness among Adolescents: The Mediating Role of Lifestyle Habits
- PMID: 35270269
- PMCID: PMC8909314
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19052576
The Effect of Problematic Social Media Use on Happiness among Adolescents: The Mediating Role of Lifestyle Habits
Abstract
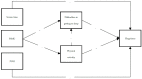
Background: Although the relationship between problematic social media use (PSMU) and happiness has been already explored, less is known about the mechanisms that translate PSMU into lower happiness through lifestyle habits. Therefore, the current study focuses on the association between PSMU and happiness, exploring a mediating effect of lifestyle habits (e.g., difficulties in getting to sleep and frequency of physical activity) among Italian adolescents. Methods: A total of 58,976 Italian adolescents (mean age = 13.6, SD = 1.63; age range = 10.5−16.5; 49.4% females) were included. The pattern of relationships specified by the theoretical model was examined through path analysis. Results: Difficulties in getting to sleep (β = −0.037, p < 0.001) and frequency of physical activity (β = −0.012, p < 0.001) were mediators in the relationship between PSMU and happiness. Multi-group analyses across gender and age groups (11, 13, and 15 years old) showed that the chain mediating effect of the frequency of physical activity on the difficulties in getting to sleep was not significant for females but significant for males and for all of the three age groups. Overall, females and older ages were sensitive to the whole model. Conclusion: Along with difficulties in getting to sleep and the frequency of physical activity, lifestyle habits may contribute to the association between PSMU and happiness. We also recommend that future studies focus on PSMU in females and older adolescents, as they show more general sleep problems and reduced physical activity.
Keywords: happiness; path analysis; physical activity; problematic social media use; sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Austin-McCain M. An examination of the association of social media use with the satisfaction with daily routines and healthy lifestyle habits for undergraduate and graduate students. Open J. Occup. Ther. 2017;5:6. doi: 10.15453/2168-6408.1327. - DOI
-
- Chen H.T., Li X.Q. The contribution of mobile social media to social capital and psychological well-being: Examining the role of communicative use, friending and self-disclosure. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017;75:958–965. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.06.011. - DOI
-
- Marengo D., Montag C., Sindermann C., Elhai J.D., Settanni M. Examining the links between active Facebook use, received likes, self-esteem and happiness: A study us-ing objective social media data. Telemat. Inform. 2021;58:101523. doi: 10.1016/j.tele.2020.101523. - DOI
-
- Wirtz D., Tucker A., Briggs C., Schoemann A.M. How and why social media affect subjective well-being: Multi-site use and social comparison as predictors of change across time. J. Happiness Stud. 2021;22:1673–1691. doi: 10.1007/s10902-020-00291-z. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

