ColaborAtiva: A Platform Based on Gamified Collaborative Practices to Prevent Pressure Injuries for Wheelchair Users
- PMID: 35270884
- PMCID: PMC8915050
- DOI: 10.3390/s22051738
ColaborAtiva: A Platform Based on Gamified Collaborative Practices to Prevent Pressure Injuries for Wheelchair Users
Abstract
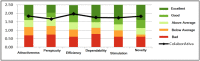
Pressure injuries are wounds caused by reduced blood circulation for regular and repetitive periods when pressing the human body against a hard surface. It is a pathology that needs daily preventive care and health promotion to avoid incidences. Thus, this article aims to validate a platform based on the gamified collaborative practices model to prevent pressure injuries. The methodological contribution is Design Science, and the software was evaluated by 16 wheelchair users who aimed at usability (SUS), user experience (UEQ), and ability to promote the system (NPS). In addition to creating a collaborative network using the interactions that occurred during the platform's use. Wheelchair users rated 73.28 for SUS; on the UEQ benchmark scales, they classified: excellent (efficiency, dependability, stimulation, and novelty), good (attractiveness), and above-average (perspicuity) and in NPS obtained 62.5%. Moreover, they provided feedback to improve and legitimize that gamification positively interfered in the execution of collaborative practices. In the end, it is possible to suppose that the prototype contributes to the prevention of pressure injuries. In addition, it is possible to adapt it to apply to other pathologies that require continuous health care such as diabetes, mental illness, heart disease, addictions, multiple sclerosis, cancer, among others, maximizing its purpose.
Keywords: ColaborAtiva; NPS; SUS; UEQ; collaborative practices; gamification; m-health; platform; pressure injury; social network analysis; wheelchair users.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


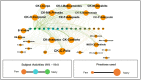
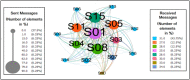
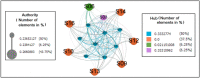

References
-
- Wolff K., Johnson R.A., Saavedra A.P. Fitzpatrick Atlas de Dermatología Clínica. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Education; Santa Fé, México: 2014.
-
- Dziedzic M.E. Fast Facts About Pressure Ulcer Care for Nurses: How to Prevent, Detect, and Resolve Them in a Nutshell. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2014.
-
- Da Saúde M. Protocolo Para Prevenção de Úlcera por Pressão. Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária; Brasília, Brazil: 2013.
-
- Silvestre J.T., Holsbach D.R. Atuação Fisioterapêutica na Úlcera de Pressão: Uma Revisão de Literatura. [(accessed on 5 February 2022)];Rev. Fafibe-Line. 2012 :1–12. Available online: http://www.unifafibe.com.br/revistasonline/arquivos/revistafafibeonline/....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

