Security Requirements and Challenges of 6G Technologies and Applications
- PMID: 35271113
- PMCID: PMC8914636
- DOI: 10.3390/s22051969
Security Requirements and Challenges of 6G Technologies and Applications
Abstract
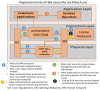
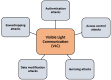
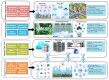
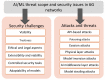
After implementing 5G technology, academia and industry started researching 6th generation wireless network technology (6G). 6G is expected to be implemented around the year 2030. It will offer a significant experience for everyone by enabling hyper-connectivity between people and everything. In addition, it is expected to extend mobile communication possibilities where earlier generations could not have developed. Several potential technologies are predicted to serve as the foundation of 6G networks. These include upcoming and current technologies such as post-quantum cryptography, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), enhanced edge computing, molecular communication, THz, visible light communication (VLC), and distributed ledger (DL) technologies such as blockchain. From a security and privacy perspective, these developments need a reconsideration of prior security traditional methods. New novel authentication, encryption, access control, communication, and malicious activity detection must satisfy the higher significant requirements of future networks. In addition, new security approaches are necessary to ensure trustworthiness and privacy. This paper provides insights into the critical problems and difficulties related to the security, privacy, and trust issues of 6G networks. Moreover, the standard technologies and security challenges per each technology are clarified. This paper introduces the 6G security architecture and improvements over the 5G architecture. We also introduce the security issues and challenges of the 6G physical layer. In addition, the AI/ML layers and the proposed security solution in each layer are studied. The paper summarizes the security evolution in legacy mobile networks and concludes with their security problems and the most essential 6G application services and their security requirements. Finally, this paper provides a complete discussion of 6G networks' trustworthiness and solutions.
Keywords: 6G security; AI/ML security; new challenges; physical layer security; privacy; security architecture; security threats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Khan R., Kumar P., Jayakody D., Liyanage M. A Survey on Security and Privacy of 5G Technologies: Potential Solutions, Recent Advancements, and Future Directions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020;22:196–248. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2019.2933899. - DOI
-
- Yazar A., Dogan-Tusha S., Arslan H. 6G vision: An ultra-flexible perspective, ITU. J. Future Evol. Technol. 2020;1:121–140.
-
- Alwis C., Kalla A., Pham Q.-V., Kumar P., Dev K., Hwang W.-J., Liyanage M. Survey on 6G Frontiers: Trends, Applications, Requirements, Technologies and Future Research. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2021;2:836–886. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2021.3071496. - DOI
-
- Ray P., Kumar N., Guizani M. A Vision on 6G-Enabled NIB: Requirements, Technologies, Deployments, and Prospects. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021;28:120–127. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2000384. - DOI
-
- Gui G., Liu M., Tang F., Kato N., Adachi F. 6G: Opening new horizons for integration of comfort, security, and intelligence. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2020;27:126–132. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1900516. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

