Macrophage-produced VEGFC is induced by efferocytosis to ameliorate cardiac injury and inflammation
- PMID: 35271504
- PMCID: PMC9057589
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI140685
Macrophage-produced VEGFC is induced by efferocytosis to ameliorate cardiac injury and inflammation
Abstract
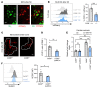
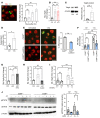
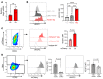
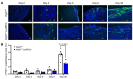
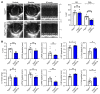
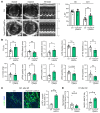
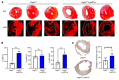
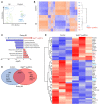
Clearance of dying cells by efferocytosis is necessary for cardiac repair after myocardial infarction (MI). Recent reports have suggested a protective role for vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) during acute cardiac lymphangiogenesis after MI. Here, we report that defective efferocytosis by macrophages after experimental MI led to a reduction in cardiac lymphangiogenesis and Vegfc expression. Cell-intrinsic evidence for efferocytic induction of Vegfc was revealed after adding apoptotic cells to cultured primary macrophages, which subsequently triggered Vegfc transcription and VEGFC secretion. Similarly, cardiac macrophages elevated Vegfc expression levels after MI, and mice deficient for myeloid Vegfc exhibited impaired ventricular contractility, adverse tissue remodeling, and reduced lymphangiogenesis. These results were observed in mouse models of permanent coronary occlusion and clinically relevant ischemia and reperfusion. Interestingly, myeloid Vegfc deficiency also led to increases in acute infarct size, prior to the amplitude of the acute cardiac lymphangiogenesis response. RNA-Seq and cardiac flow cytometry revealed that myeloid Vegfc deficiency was also characterized by a defective inflammatory response, and macrophage-produced VEGFC was directly effective at suppressing proinflammatory macrophage activation. Taken together, our findings indicate that cardiac macrophages promote healing through the promotion of myocardial lymphangiogenesis and the suppression of inflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: Inflammation; Innate immunity; Macrophages; Molecular pathology; Vascular Biology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Macrophage efferocytosis with VEGFC and lymphangiogenesis: rescuing the broken heart.J Clin Invest. 2022 May 2;132(9):e158703. doi: 10.1172/JCI158703. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35499075 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Macrophage efferocytosis with VEGFC and lymphangiogenesis: rescuing the broken heart.J Clin Invest. 2022 May 2;132(9):e158703. doi: 10.1172/JCI158703. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35499075 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced efferocytosis of apoptotic cardiomyocytes through myeloid-epithelial-reproductive tyrosine kinase links acute inflammation resolution to cardiac repair after infarction.Circ Res. 2013 Sep 27;113(8):1004-12. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301198. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23836795 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphatic and Immune Cell Cross-Talk Regulates Cardiac Recovery After Experimental Myocardial Infarction.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Jul;40(7):1722-1737. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314370. Epub 2020 May 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32404007 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages in the Inflammatory Phase following Myocardial Infarction: Role of Exogenous Ubiquitin.Biology (Basel). 2023 Sep 20;12(9):1258. doi: 10.3390/biology12091258. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37759657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac macrophages and emerging roles for their metabolism after myocardial infarction.J Clin Invest. 2023 Sep 15;133(18):e171953. doi: 10.1172/JCI171953. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37712418 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N-n-butyl haloperidol iodide mediates cardioprotection via regulating AMPK/FoxO1 signalling.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jan;28(2):e18049. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18049. Epub 2023 Nov 21. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37987145 Free PMC article.
-
hESC-Derived Epicardial Cells Promote Repair of Infarcted Hearts in Mouse and Swine.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Sep;10(27):e2300470. doi: 10.1002/advs.202300470. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37505480 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of secretome from porcine cardiosphere-derived cells on porcine macrophage polarization and their possible implications for cardiac remodeling post-myocardial infarction in vitro.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 30;13:1601743. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1601743. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40661150 Free PMC article.
-
Primitive macrophages induce sarcomeric maturation and functional enhancement of developing human cardiac microtissues via efferocytic pathways.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024 May;3(5):567-593. doi: 10.1038/s44161-024-00471-7. Epub 2024 May 7. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 39086373 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage Polarization in Myocardial Ischemia‒Reperfusion Injury: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Targets.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jul 31;19:6519-6541. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S516001. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40766819 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

