Prevalence of oral manifestations in COVID-19: A systematic review
- PMID: 35271738
- PMCID: PMC9111150
- DOI: 10.1002/rmv.2345
Prevalence of oral manifestations in COVID-19: A systematic review
Abstract
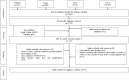
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a novel disease caused by a newly identified virus Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) causing diverse systemic manifestations. The oral cavity too is not spared and the symptoms appear either independently, concurrently, or sequentially. In view of the rising documented cases of oral lesions of COVID-19, this systematic review aims to assess the prevalence of oral manifestations in COVID-19 confirmed individuals. An extensive literature search was conducted in databases like Scopus, Pubmed/Medline, Livivo, Lilacs and Google Scholar and varied oral signs and symptoms were reported as per the PRISMA guidelines. Studies published in English language literature only were included and were subjected to the risk of bias using the Joana Briggs Institute Appraisal tools for prevalence studies, case series and case reports. In a two-phase selection, 34 studies were included: 21 observational, 3 case-series and 10 case reports. These observational studies included approximately 14,003 patients from 10 countries. In this review, we explored the most commonly encountered oral and dental manifestations in COVID-19 and identified that loss of taste acuity, xerostomia and anosmia were frequently reported. Elevated incidence of opportunistic infections like mucormycosis and aspergillosis were reported during the treatment due to prolonged intake of steroids. Immunosuppression and poor oral hygiene led to secondary manifestations like enanthematous lesions. However, it is not clear that oral signs and symptoms are due to COVID-19 infection itself or are the result of extensive treatment regimen followed [PROSPERO CRD42021258264].
Keywords: Covid-19; SARS-CoV-2 infection; oral manifestations.
© 2022 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-neutralising monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 2;9(9):CD013825. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013825.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34473343 Free PMC article.
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of COVID-19 Disease on the Development of Osteomyelitis of Jaws: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 23;13(15):4290. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154290. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk indicators for oral ulcers among people living with HIV during the first wave of the pandemic: a cross sectional study.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Aug 27;23(1):600. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03330-2. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37635219 Free PMC article.
-
The Oral Lesion in the COVID-19 Patient: Is It True Oral Manifestation or Not?Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Jul 4;16:4357-4385. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S411615. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37424667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiology of oral lesions subsequent to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: A systematic review.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2024 Jul-Sep;28(3):443-454. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.jomfp_511_23. Epub 2024 Oct 15. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39670118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Manifestations in the Post COVID-19 Condition: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis.Rev Med Virol. 2025 Jul;35(4):e70057. doi: 10.1002/rmv.70057. Rev Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 40663038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous