Efficacy of an Esophageal Spacer for Spine Radiosurgery: First Experience
- PMID: 35272076
- PMCID: PMC9232906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prro.2022.02.010
Efficacy of an Esophageal Spacer for Spine Radiosurgery: First Experience
Abstract
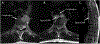
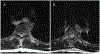
This is the first study to investigate the use of an esophageal hydrogel spacer in spine stereotactic radiosurgery. The tolerability and the dose reduction to the esophagus are predicted to reduce the incidence of high-grade toxicities, which in turn can permit dose escalation to optimize tumor control.
Copyright © 2022 American Society for Radiation Oncology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Glicksman RM, Tjong MC, Neves-Junior WFP, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the management of spinal metastases: A review. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6:567–577. - PubMed
-
- Mariados N, Sylvester J, Shah D, et al. Hydrogel spacer prospective multicenter randomized controlled pivotal trial: Dosimetric and clinical effects of perirectal spacer application in men undergoing prostate image guided intensity modulated radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;92:971–977. - PubMed
-
- Pinkawa M, Piroth MD, Holy R, et al. Spacer stability and prostate position variability during radiotherapy for prostate cancer applying a hydrogel to protect the rectal wall. Radiother Oncol. 2013;106:220–224. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

