A severe microsporidian disease in cultured Atlantic Bluefin Tuna (Thunnus thynnus)
- PMID: 35272715
- PMCID: PMC8915461
- DOI: 10.1186/s43008-022-00090-6
A severe microsporidian disease in cultured Atlantic Bluefin Tuna (Thunnus thynnus)
Abstract
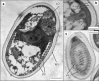
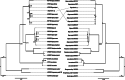
One of the most promising aquaculture species is the Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) with high market value; disease control is crucial to prevent and reduce mortality and monetary losses. Microsporidia (Fungi) are a potential source of damage to bluefin tuna aquaculture. A new microsporidian species is described from farmed bluefin tunas from the Spanish Mediterranean. This new pathogen is described in a juvenile associated with a highly severe pathology of the visceral cavity. Whitish xenomas from this microsporidian species were mostly located at the caecal mass and ranged from 0.2 to 7.5 mm. Light and transmission electron microscopy of the spores revealed mature spores with an average size of 2.2 × 3.9 μm in size and a polar filament with 13-14 coils arranged in one single layer. Phylogenetic analysis clustered this species with the Glugea spp. clade. The morphological characteristics and molecular comparison confirm that this is a novel microsporidian species, Glugea thunni. The direct life-cycle and the severe pathologies observed makes this parasite a hard risk for bluefin tuna cultures.
Keywords: Aquaculture; Glugea thunni new taxa; Glugeida; Marinosporidia; Microsporidia; Osteichthyes; Scombridae; Xenoma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Abdel-Baki AAS, Al-Quraishy S, Rocha S, Dkhil MA, Casal G, Azevedo C. Ultrastructure and phylogeny of Glugea nagelia n. sp. (Microsporidia: Glugeidae), infecting the intestinal wall of the yellowfin hind, Cephalopholis hemistiktos (Actinopterygii: Serranidae), from the Red Sea. Folia Parasitologica. 2015;62(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Baki AAS, Tamihi AF, Al-Qahtani HA, Al-Quraishy S, Mansour L. Glugea jazanensis sp. Nov. infecting Lutjanus bohar in the Red Sea: ultrastructure and phylogeny. Dis Aquat Organ. 2015;116(3):185–190. - PubMed
-
- APROMAR (2020) Aquaculture in Spain 2020 Asociación Empresarial de Productores de Cultivos Marinos. Chiclana (Cádiz). http://www.apromar.es/content/informes-anuales
-
- Azevedo C, Abdel-Baki AAS, Rocha S, Al-Quraishy S, Casal G. Ultrastructure and phylogeny of Glugea arabica n. sp. (Microsporidia), infecting the marine fish Epinephelus polyphekadion from the Red Sea. Eur J Protistol. 2016;52(228):11–21. - PubMed
-
- Bell AS, Aoki T, Yokoyama H. Phylogenetic relationships among microsporidia based on rDNA sequence data, with particular reference to fish-infecting Microsporidium Balbiani 1884 species. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2001;48(3):258–265. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
