Cooperation Between Systemic and Mucosal Antibodies Induced by Virosomal Vaccines Targeting HIV-1 Env: Protection of Indian Rhesus Macaques Against Low-Dose Intravaginal SHIV Challenges
- PMID: 35273592
- PMCID: PMC8902080
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.788619
Cooperation Between Systemic and Mucosal Antibodies Induced by Virosomal Vaccines Targeting HIV-1 Env: Protection of Indian Rhesus Macaques Against Low-Dose Intravaginal SHIV Challenges
Abstract
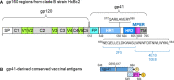
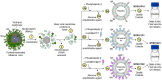
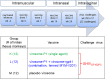
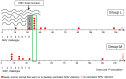
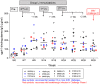
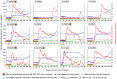
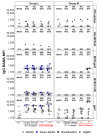
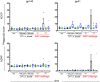
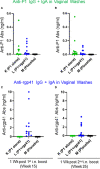
A virosomal vaccine inducing systemic/mucosal anti-HIV-1 gp41 IgG/IgA had previously protected Chinese-origin rhesus macaques (RMs) against vaginal SHIVSF162P3 challenges. Here, we assessed its efficacy in Indian-origin RMs by intramuscular priming/intranasal boosting (n=12/group). Group K received virosome-P1-peptide alone (harboring the Membrane Proximal External Region), Group L combined virosome-rgp41 plus virosome-P1, and Group M placebo virosomes. Vaccination induced plasma binding but no neutralizing antibodies. Five weeks after boosting, all RMs were challenged intravaginally with low-dose SHIVSF162P3 until persistent systemic infection developed. After SHIV challenge #7, six controls were persistently infected versus only one Group L animal (vaccine efficacy 87%; P=0.0319); Group K was not protected. After a 50% SHIV dose increase starting with challenge #8, protection in Group L was lost. Plasmas/sera were analyzed for IgG phenotypes and effector functions; the former revealed that protection in Group L was significantly associated with increased binding to FcγR2/3(A/B) across several time-points, as were some IgG measurements. Vaginal washes contained low-level anti-gp41 IgGs and IgAs, representing a 1-to-5-fold excess over the SHIV inoculum's gp41 content, possibly explaining loss of protection after the increase in challenge-virus dose. Virosomal gp41-vaccine efficacy was confirmed during the initial seven SHIV challenges in Indian-origin RMs when the SHIV inoculum had at least 100-fold more HIV RNA than acutely infected men's semen. Vaccine protection by virosome-induced IgG and IgA parallels the cooperation between systemically administered IgG1 and mucosally applied dimeric IgA2 monoclonal antibodies that as single-agents provided no/low protection - but when combined, prevented mucosal SHIV transmission in all passively immunized RMs.
Keywords: HIV-1 gp41; Indian-origin rhesus macaque model; SHIV; intramuscular prime/intranasal boost vaccination; intravaginal challenge; mucosal immunity; virosomal vaccine; virosomes.
Copyright © 2022 Lakhashe, Amacker, Hariraju, Vyas, Morrison, Weiner, Ackerman, Roy, Alter, Ferrari, Montefiori, Tomaras, Sawant, Yates, Gast, Fleury and Ruprecht.
Conflict of interest statement
MA and SF are employees of Mymetics SA. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Pitisuttithum P, Gilbert P, Gurwith M, Heyward W, Martin M, van Griensven F, et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Efficacy Trial of a Bivalent Recombinant Glycoprotein 120 HIV-1 Vaccine Among Injection Drug Users in Bangkok, Thailand. J Infect Dis (2006) 194(12):1661–71. doi: 10.1086/508748 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

