Development and Validation of a Novel Stemness-Index-Related Long Noncoding RNA Signature for Breast Cancer Based on Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
- PMID: 35273635
- PMCID: PMC8902307
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.760514
Development and Validation of a Novel Stemness-Index-Related Long Noncoding RNA Signature for Breast Cancer Based on Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
Abstract
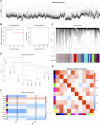
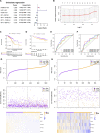
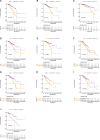
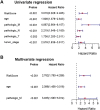
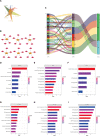
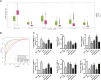
Background: Breast cancer (BC) is a major leading cause of woman deaths worldwide. Increasing evidence has revealed that stemness features are related to the prognosis and progression of tumors. Nevertheless, the roles of stemness-index-related long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in BC remain unclear. Methods: Differentially expressed stemness-index-related lncRNAs between BC and normal samples in The Cancer Genome Atlas database were screened based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis and differential analysis. Univariate Cox and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression analyses were performed to identify prognostic lncRNAs and construct a stemness-index-related lncRNA signature. Time-dependent receiver operating characteristic curves were plotted to evaluate the predictive capability of the stemness-index-related lncRNA signature. Moreover, correlation analysis and functional enrichment analyses were conducted to investigate the stemness-index-related lncRNA signature-related biological function. Finally, a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to detect the expression levels of lncRNAs. Results: A total of 73 differentially expressed stemness-index-related lncRNAs were identified. Next, FAM83H-AS1, HID1-AS1, HOXB-AS1, RP11-1070N10.3, RP11-1100L3.8, and RP11-696F12.1 were used to construct a stemness-index-related lncRNA signature, and receiver operating characteristic curves indicated that stemness-index-related lncRNA signature could predict the prognosis of BC well. Moreover, functional enrichment analysis suggested that differentially expressed genes between the high-risk group and low-risk group were mainly involved in immune-related biological processes and pathways. Furthermore, functional enrichment analysis of lncRNA-related protein-coding genes revealed that FAM83H-AS1, HID1-AS1, HOXB-AS1, RP11-1070N10.3, RP11-1100L3.8, and RP11-696F12.1 were associated with neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, AMPK signaling pathway, PPAR signaling pathway, and cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. Finally, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction revealed that FAM83H-AS1, HID1-AS1, RP11-1100L3.8, and RP11-696F12.1 might be used as the potential diagnostic biomarkers of BC. Conclusion: The stemness-index-related lncRNA signature based on FAM83H-AS1, HID1-AS1, HOXB-AS1, RP11-1070N10.3, RP11-1100L3.8, and RP11-696F12.1 could be used as an independent predictor for the survival of BC, and FAM83H-AS1, HID1-AS1, RP11-1100L3.8, and RP11-696F12.1 might be used as the diagnostic markers of BC.
Keywords: WGCNA; breast cancer; cancer stem cells; prognosis; stemness-index-related lncRNAs.
Copyright © 2022 Qian, Qian, Ye, Xu, Wu, Li, Li, Yu and Tao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

