Oxygen desaturation index as alternative parameter in screening patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 35273770
- PMCID: PMC8889990
- DOI: 10.5935/1984-0063.20200119
Oxygen desaturation index as alternative parameter in screening patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
Objectives: Assess reliability of oxygen desaturation index (ODI) as an alternative parameter to apnea hypopnea index (AHI) in screening patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Material and methods: Retrospectively two-year data on demography, anthropometric features, polysomnography (PSG) parameters [AHI, ODI, minimum oxygen saturation (SpO2), mean SpO2], and Epworth sleepiness score (ESS) were collected and analyzed.
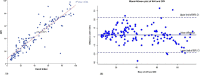
Results: Study showed significant correlation of ESS with AHI, ODI, apnea-hypopnea percentage of sleep period time (AH%SPT), mean SpO2 and minimum SpO2 with highest correlation being with AHI. A Cohen's weighted Kappa analysis showed good concordance of 87.32% between AHI and ODI in classifying severity of OSA, with a significant R2 correlation of 0.84 on linear regression. An ODI>20 has a sensitivity of 96.6% and specificity of 69.6% in diagnosing severe OSA.
Conclusion: Good concordance between AHI and ODI makes nocturnal oximetry a less expensive tool to confdently screen patients with severe OSA.
Keywords: Apnea Hypopnea Index; Obstructive Sleep Apnea; Oxygen Desaturation Index; Sleepiness.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no confict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Johns MW. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep. 1991 Dec;14(6):540–545. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
