Characterization of cyclic alternating pattern in infants with laryngomalacia
- PMID: 35273771
- PMCID: PMC8889959
- DOI: 10.5935/1984-0063.20210017
Characterization of cyclic alternating pattern in infants with laryngomalacia
Abstract
Objective: Cyclic alternanting pattern (CAP) has been considered a marker of sleep instability in children. The aim of this study was to evaluate the CAP in infants with laryngomalacia.
Material and methods: CAP were quantified in 15 infants with laryngomalacia (mean age 167.2±97.21 days) and 10 controls (mean age of 158.5±116.2 days) using polysomnography.
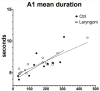
Results: The distribution of the A2 subtypes across NREM stages in infants with laryngomalacia showed a decrease, as well as in the mean duration of CAP sequences. The A3 CAP and arousals increased in infants with laryngomalacia. Our data showed a stronger correlation between the mean duration of A1 CAP and the age in healthy controls than in infants with laryngomalacia. In accordance to previous reports infants with laryngomalacia exhibited an increase in total awake time, apnea-hypopnea index, and a decrease in N3 stage compared to controls.
Discussion: Our findings add to a growing body of literature of CAP as an indicator of brain maturation.
Keywords: Apnea; Diseases; Infant; Laryngomalacia; Newborn; Sleep.
Figures
References
-
- Terzano MG, Mancia D, Salati MR, Costani G, Decembrino A, Parrino L. The cyclic alternating pattern as a physiologic component of normal NREM sleep. Sleep. 1985;8(2):137–145. - PubMed
-
- Santana-Miranda R, Murata C, Bruni O, Rosa A, Alvarado-Ruiz G, Castillo-Montoya CR, et al. Cyclic alternating pattern in infants with congenital hypothyroidism. Brain Dev. 2019 Jan;41(1):66–71. - PubMed
-
- Milano S, Castaldo R, Ferri R, Peraita-Adrados R, Paolino MC, Montesano M, et al. Sleep cyclic alternating pattern analysis in infants with apparent life-threatening events: a daytime polysomnographic study. Clin Neurophysiol. 2012 Jul;123(7):1346–1352. - PubMed
-
- Bruni O, Novelli L, Luchetti A, Zarowski M, Meloni M, Cecili M, et al. Reduced NREM sleep instability in benign childhood epilepsy with centro-temporal spikes. Clin Neurophysiol. 2010 Jan;121(5):665–671. - PubMed
-
- Miano S, Bruni O, Elia M, Scifo L, Smerieri A, Trovato A, et al. Sleep phenotypes of intellectual disability: a polysomnographic evaluation in subjects with Down syndrome and Fragile-X syndrome. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008 Apr;119(6):1242–1247. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
