Exosomal miR-29b of Gut Origin in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis Suppresses Heart Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
- PMID: 35274002
- PMCID: PMC8902158
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.759689
Exosomal miR-29b of Gut Origin in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis Suppresses Heart Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
Abstract
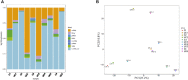
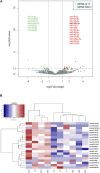
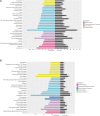
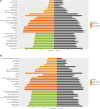
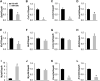
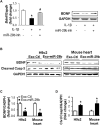
Background and Aims: While the interplay between heart and gut in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has previously been noted, how the inflamed gut impairs heart function remain elusive. We hypothesized that exosomal miRNAs of gut origin induce cardiac remodeling in IBD. Our aim was to identify plasma exosomal miRNAs that not only are of diagnostic value but also contribute to cardiac remodeling in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). Methods: Plasma exosomes were isolated from UC patients and healthy control subjects and exosomal miRNAs were profiled by next-generation sequencing. Exosomal miR-29b levels in CCD841 CoN colon epithelial cells were detected by RT-qPCR. Exosomes packaged with miR-29b were incubated with H9c2 cells or administered to live mice. Results: The plasma exosomal miRNA profiles of the UC patients were significantly different from that of the controls and 20 miRNAs including miR-29b were differentially expressed. In CCD841 CoN cells, TNFα, IL-1β, and H2O2 significantly elevated miR-29b in both the cells and their secreted exosomes (p < 0.01), suggesting that intestinal epithelium secrets exosomes rich in miR-29b in IBD. In H9c2 myoblast cells, miR-29b modulated multiple genes including brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Epithelial cell-derived exosomes packaged with miR-29b also attenuated BDNF and increased cleaved caspase 3, suggestive of apoptosis. Furthermore, tail vein injection of engineered exosomes with high levels of miR-29b suppressed BDNF and augmented cleaved caspase 3 in the heart of adult mouse (p < 0.01). Conclusion: Plasma exosomal miRNA profile could be a novel diagnostic approach for IBD. Excessive plasma exosomal miR-29b suppresses critical proteins like BDNF in IBD, leading to cardiac impairment.
Keywords: cardiac remodeling; exosome; inflammatory bowel disease; microRNA; pro-inflammatory cytokine.
Copyright © 2022 Lian, Zhong, Xiao, Sun, Shen, Zhao, Ma, Li, Niu, Liu, Powell, Liu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fasseu M., Tréton X., Guichard C., Pedruzzi E., Cazals-Hatem D., Richard C., et al. (2010). Identification of Restricted Subsets of Mature microRNA Abnormally Expressed in Inactive Colonic Mucosa of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. PLoS One 5 (10), e13160. 10.1371/journal.pone.0013160 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

