Fructus Amomi extract attenuates nasal inflammation by restoring Th1/Th2 balance and down-regulation of NF-κB phosphorylation in OVA-induced allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 35274678
- PMCID: PMC8935377
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20212681
Fructus Amomi extract attenuates nasal inflammation by restoring Th1/Th2 balance and down-regulation of NF-κB phosphorylation in OVA-induced allergic rhinitis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Fructus Amomi extract attenuates nasal inflammation by restoring Th1/Th2 balance and downregulation of NF-kB phosphorylation in OVA-induced allergic rhinitis.Biosci Rep. 2023 May 31;43(5):BSR-2021-2681_COR. doi: 10.1042/BSR-2021-2681_COR. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37218503 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
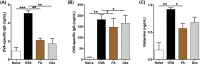
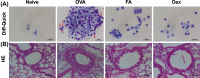
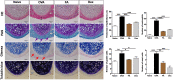
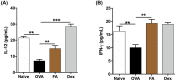
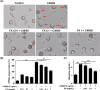
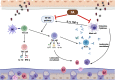
Fructus Amomi Cardamomi (FA) is the mature fruit of Amomum villosum Lour (family Zingiberaceae) and is commonly used in Chinese traditional medicine to treat various gastrointestinal disorders. FA's possible benefits as an allergic rhinitis (AR) treatment, however, have not been examined. We used an ovalbumin (OVA)-induced AR mouse model to identify any anti-allergic effects associated with the administration of 200 mg/kg FA or dexamethasone (Dex) 2.5 mg/kg by oral administration. The results of our testing confirm that FA ameliorated nasal symptoms and alleviated nasal epithelium swelling, reduced the goblet cell hyperplasia and eosinophil cell infiltration in the nasal epithelium, and inhibited lung tissue inflammation and Dex as well. Significantly decreased Th2 cytokine (interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-4, and IL-5) expression, and a correspondingly significant increase in Th1 cytokine (IL-12, interferon (IFN)-γ) production, was observed in nasal lavage fluid (NALF) taken from mice that received FA or Dex treatment. FA also reduced the presence of OVA-specific immunoglobulin (Ig) E, OVA-specific IgG1, and histamine levels in serum, and inhibited mast cell degranulation in vitro. In addition, these effects were involved with the reduction in NF-κB phosphorylation. These results suggest that FA restores Th1/Th2 balance and inhibits NF-κB phosphorylation and mast cell degranulation, thereby achieving a notable anti-inflammatory effect. Accordingly, it has the potential to be used as an efficacious therapeutic treatment for AR.
Keywords: Fructus Amomi; NF-κB phosphorylation; Th1/Th2 balance; allergic rhinitis; mast cell degranulation.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Saikosaponin A ameliorates nasal inflammation by suppressing IL-6/ROR-γt/STAT3/IL-17/NF-κB pathway in OVA-induced allergic rhinitis.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 Jan 5;315:108874. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108874. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 31669322
-
Apigenin attenuates inflammatory response in allergic rhinitis mice by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.Environ Toxicol. 2023 Feb;38(2):253-265. doi: 10.1002/tox.23699. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Environ Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36350155
-
Skullcapflavone II attenuates ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis through the blocking of Th2 cytokine production and mast cell histamine release.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Nov;52:77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.08.029. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28886581
-
Research Progress on the Mechanism of Acupuncture in the Prevention and Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis.Altern Ther Health Med. 2023 Nov;29(8):228-232. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023. PMID: 37573594 Review.
-
The potential application and molecular mechanisms of natural products in the treatment of allergic rhinitis: A review.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul;129:155663. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155663. Epub 2024 Apr 21. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38759345 Review.
Cited by
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis exacerbates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by driving Th1 differentiation via ZAP70/NF-κB signaling.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 18;16:1549102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1549102. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40170858 Free PMC article.
-
Caesalpinia sappan Linn. Ameliorates Allergic Nasal Inflammation by Upregulating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in an Allergic Rhinitis Mouse Model and Nasal Epithelial Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;11(11):2256. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112256. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421442 Free PMC article.
-
Constructing a competitive endogenous RNA network of EndMT-related atherosclerosis through weighted gene co-expression network analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 10;10:1322252. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1322252. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38268851 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and experimental analysis to reveal the mechanism of Dan-Shen-Yin against endothelial to mesenchymal transition in atherosclerosis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 24;13:946193. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.946193. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091823 Free PMC article.
-
Fallopia japonica Root Extract Ameliorates Ovalbumin-Induced Airway Inflammation in a CARAS Mouse Model by Modulating the IL-33/TSLP/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 7;24(15):12514. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512514. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachert C., Jorissen M., Bertrand B., Khaltaev N. and Bousquet J. (2008) Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma update (ARIA 2008). The Belgian Perspect. 4, 253–257 - PubMed
-
- Sacre Hazouri J.A. (2006) [Allergic rhinitis. Coexistent diseases and complications. A review and analysis]. Rev. Alerg. Mex. 53, 9–29 - PubMed
-
- Kirmaz C., Bayrak P., Yilmaz O. and Yuksel H. (2005) Effects of glucan treatment on the Th1/Th2 balance in patients with allergic rhinitis: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 16, 128–134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

