Systemic interventions for treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS/TEN overlap syndrome
- PMID: 35274741
- PMCID: PMC8915395
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013130.pub2
Systemic interventions for treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS/TEN overlap syndrome
Abstract
Background: Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS/TEN overlap syndrome are rare, severe cutaneous adverse reactions usually triggered by medications. In addition to tertiary-level supportive care, various systemic therapies have been used including glucocorticoids, intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIGs), cyclosporin, N-acetylcysteine, thalidomide, infliximab, etanercept, and plasmapheresis. There is an unmet need to understand the efficacy of these interventions.
Objectives: To assess the effects of systemic therapies (medicines delivered orally, intramuscularly, or intravenously) for the treatment of SJS, TEN, and SJS/TEN overlap syndrome.
Search methods: We searched the following databases up to March 2021: the Cochrane Skin Specialised Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and Embase. We also searched five clinical trial registers, the reference lists of all included studies and of key review articles, and a number of drug manufacturer websites. We searched for errata or retractions of included studies.
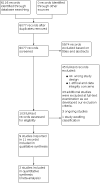
Selection criteria: We included only randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and prospective observational comparative studies of participants of any age with a clinical diagnosis of SJS, TEN, or SJS/TEN overlap syndrome. We included all systemic therapies studied to date and permitted comparisons between each therapy, as well as between therapy and placebo.
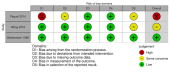
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures as specified by Cochrane. Our primary outcomes were SJS/TEN-specific mortality and adverse effects leading to discontinuation of SJS/TEN therapy. Secondary outcomes included time to complete re-epithelialisation, intensive care unit length of stay, total hospital length of stay, illness sequelae, and other adverse effects attributed to systemic therapy. We rated the certainty of the evidence for each outcome using GRADE.
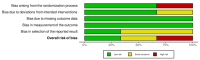
Main results: We included nine studies with a total of 308 participants (131 males and 155 females) from seven countries. We included two studies in the quantitative meta-analysis. We included three RCTs and six prospective, controlled observational studies. Sample sizes ranged from 10 to 91. Most studies did not report study duration or time to follow-up. Two studies reported a mean SCORe of Toxic Epidermal Necrosis (SCORTEN) of 3 and 1.9. Seven studies did not report SCORTEN, although four of these studies reported average or ranges of body surface area (BSA) (means ranging from 44% to 51%). Two studies were set in burns units, two in dermatology wards, one in an intensive care unit, one in a paediatric ward, and three in unspecified inpatient units. Seven studies reported a mean age, which ranged from 29 to 56 years. Two studies included paediatric participants (23 children). We assessed the results from one of three RCTs as low risk of bias in all domains, one as high, and one as some concerns. We judged the results from all six prospective observational comparative studies to be at a high risk of bias. We downgraded the certainty of the evidence because of serious risk of bias concerns and for imprecision due to small numbers of participants. The interventions assessed included systemic corticosteroids, tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors, cyclosporin, thalidomide, N-acetylcysteine, IVIG, and supportive care. No data were available for the main comparisons of interest as specified in the review protocol: etanercept versus cyclosporin, etanercept versus IVIG, IVIG versus supportive care, IVIG versus cyclosporin, and cyclosporin versus corticosteroids. Corticosteroids versus no corticosteroids It is uncertain if there is any difference between corticosteroids (methylprednisolone 4 mg/kg/day for two more days after fever had subsided and no new lesions had developed) and no corticosteroids on disease-specific mortality (risk ratio (RR) 2.55, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.72 to 9.03; 2 studies; 56 participants; very low-certainty evidence). Time to complete re-epithelialisation, length of hospital stay, and adverse effects leading to discontinuation of therapy were not reported. IVIG versus no IVIG It is uncertain if there is any difference between IVIG (0.2 to 0.5 g/kg cumulative dose over three days) and no IVIG in risk of disease-specific mortality (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.04 to 2.91); time to complete re-epithelialisation (mean difference (MD) -2.93 days, 95% CI -4.4 to -1.46); or length of hospital stay (MD -2.00 days, 95% CI -5.81 to 1.81). All results in this comparison were based on one study with 36 participants, and very low-certainty evidence. Adverse effects leading to discontinuation of therapy were not reported. Etanercept (TNF-alpha inhibitor) versus corticosteroids Etanercept (25 mg (50 mg if weight > 65 kg) twice weekly "until skin lesions healed") may reduce disease-specific mortality compared to corticosteroids (intravenous prednisolone 1 to 1.5 mg/kg/day "until skin lesions healed") (RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.16 to 1.63; 1 study; 91 participants; low-certainty evidence); however, the CIs were consistent with possible benefit and possible harm. Serious adverse events, such as sepsis and respiratory failure, were reported in 5 of 48 participants with etanercept and 9 of 43 participants with corticosteroids, but it was not clear if they led to discontinuation of therapy. Time to complete re-epithelialisation and length of hospital stay were not reported. Cyclosporin versus IVIG It is uncertain if there is any difference between cyclosporin (3 mg/kg/day or intravenous 1 mg/kg/day until complete re-epithelialisation, then tapered off (10 mg/day reduction every 48 hours)) and IVIG (continuous infusion 0.75 g/kg/day for 4 days (total dose 3 g/kg) in participants with normal renal function) in risk of disease-specific mortality (RR 0.13, 95% CI 0.02 to 0.98, 1 study; 22 participants; very low-certainty evidence). Time to complete re-epithelialisation, length of hospital stay, and adverse effects leading to discontinuation of therapy were not reported. No studies measured intensive care unit length of stay.
Authors' conclusions: When compared to corticosteroids, etanercept may result in mortality reduction. For the following comparisons, the certainty of the evidence for disease-specific mortality is very low: corticosteroids versus no corticosteroids, IVIG versus no IVIG and cyclosporin versus IVIG. There is a need for more multicentric studies, focused on the most important clinical comparisons, to provide reliable answers about the best treatments for SJS/TEN.
Copyright © 2022 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclaimer
This project was supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), via Cochrane Infrastructure funding to the Cochrane Skin Group. The views and opinions expressed therein are those of the review authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Systematic Reviews Programme, NIHR, NHS, or the Department of Health.
Figures












Comment in
-
Systemic Interventions for Treatment of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Summary of a Cochrane Review.JAMA Dermatol. 2022 Dec 1;158(12):1436-1437. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.4543. JAMA Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 36260297
-
From the Cochrane Library: Systemic Interventions for Steven-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), and SJS/TEN Overlap Syndrome.JMIR Dermatol. 2024 Jan 30;7:e46580. doi: 10.2196/46580. JMIR Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38289652 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Azfar 2010 {published data only}
-
- Azfar NA, Zia MA, Malik LM, Khan AR, Jahangir M.Role of systemic steroids in the outcome of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Journal of Pakistan Association of Dermatologists 2010;20(3):158-62.
Gonzalez‐Herrada 2017 {published and unpublished data}
-
- González-Herrada C, Rodríguez-Martín S, Cachafeiro L, Lerma V, González O, Lorente JA, et al.Cyclosporine use in epidermal necrolysis is associated with an important mortality reduction: evidence from three different approaches. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2017;137(10):2092-100. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Han 2017 {published data only}
-
- Han F, Zhang J, Guo Q, Feng Y, Gao Y, Guo L, et al.Successful treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis using plasmapheresis: a prospective observational study. Journal of Critical Care 2017;42:65-8. - PubMed
Jagadeesan 2013 {published data only}
-
- Jagadeesan S, Sobhanakumari K, Sadanandan SM, Ravindran S, Divakaran MV, Skaria L, et al.Low dose intravenous immunoglobulins and steroids in toxic epidermal necrolysis: a prospective comparative open-labelled study of 36 cases. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology 2013;79(4):506-11. - PubMed
Kakourou 1997 {published data only}
-
- Kakourou T, Klontza D, Soteropoulou F, Kattamis C.Corticosteroid treatment of erythema multiforme major (Stevens-Johnson syndrome) in children. European Journal of Pediatrics 1997;156(2):90-3. - PubMed
Paquet 2014 {published data only}
Saraogi 2016 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Agrawal P, Mahajan S, Khopkar U.Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a prospective study of epidemiology and clinical course. Allergy: European Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2013;68(Suppl 97):140.
-
- Saraogi P, Mahajan S, Khopkar U.Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a prospective study of epidemiology and clinical course. British Journal of Dermatology 2016;175(Suppl 1):46.
Wang 2018 {published data only}
Wolkenstein 1998 {published data only}
-
- Wolkenstein P, Latarget J, Roujeau JC, Duguet C, Boudeau S, Vaillant L, et al.Randomized double-blind comparison of thalidomide versus placebo in toxic epidermal necrolysis: overmortality in treated group. Journal of Dermatological Science 1998;16(Suppl 1):S44. [DOI: 10.1016/S0923-1811(98)83259-3] - DOI
-
- Wolkenstein P, Latarjet J, Roujeau JC, Duguet C, Boudeau S, Vaillant L, et al.Randomised comparison of thalidomide versus placebo in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Lancet 1998;352(9140):1586-9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Auyeung 2018 {published data only}
Campione 2003 {published data only}
-
- Campione E, Marulli GC, Carrozzo AM, Chimenti MS, Costanzo A, Bianchi L.High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin for severe drug reactions: efficacy in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2003;83(6):430-2. - PubMed
Choudhury 2008 {published data only}
Danby 2007 {published data only}
-
- Danby FW.Ciclosporin use in toxic epidermal necrolysis. British Journal of Dermatology 2007;156(2):390-1. - PubMed
De Juan 2002 {published data only}
-
- De Juan Martin F, Bouthelier Moreno M, Marin Bravo Ma C, Melendo Gimeno J.Toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with intravenous immunoglobulin. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 2002;56(4):370-1. - PubMed
Del 1996 {published data only}
-
- Del Pozo J, De Lucas R, Suarez-Marrero MC, Fernandez-Diaz ML, Casado M, Garcia-Torres V.Toxic epidermal necrolysis: treatment with cyclophosphamide. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 1996;7(2):127.
Dequidt 2019 {published data only}
-
- Dequidt L, Darrigade AS, Camus T, Taieb A, Milpied B.Intravenous immunoglobulins for delayed wound healing associated with toxic epidermal necrolysis. European Journal of Dermatology: EJD 2019;29(2):229-31. - PubMed
Dhar 1996 {published data only}
-
- Dhar S.Systemic corticosteroids in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology 1996;62(4):270-1. - PubMed
Didona 2015 {published data only}
-
- Didona B, Paradisi A, Didona D, Abeni D.Etanercept for toxic epidermal necrolysis: a confirm on efficacy and safety. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2015;1:S72.
Eliades 2020 {published data only}
-
- Eliades P, Fonseca M, Harp J.Use of etanercept in a series of pediatric patients with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome-Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis spectrum disease. JAMA Dermatology 2020;29:29. - PubMed
Feldmeyer 2011 {published data only}
-
- Feldmeyer L, Kerdel FA, French LE.Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Archives of Dermatology 2011;147(12):1440-1. - PubMed
Firoz 2012 {published data only}
-
- Editors.Erratum. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2013;69(6):1048. - PubMed
-
- Editors.Expression of Concern. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014;71(3):583. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Firoz BF, Henning JS, Zarzabal LA, Pollock BH.Toxic epidermal necrolysis: five years of treatment experience from a burn unit. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2012;67(4):630-5. - PubMed
Gomez‐Flores 2020 {published data only}
-
- Gomez-Flores M, Villarreal-Villarreal CD, Welsh O, Cardenas-de la Garza JA, Sanchez-Meza E, Ancer-Arellano J, et al.Lower than expected mortality with dexamethasone in toxic epidermal necrolysis: 30-year experience of a Northern Mexico reference hospital. International Journal of Dermatology 2020;59(1):e4-5. - PubMed
Halebian 1986 {published data only}
Hertl 1993 {published data only}
-
- Hertl M, Bohlen H, Merk HF.Efficacy of cyclophosphamide in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1993;28(3):511. - PubMed
Hirahara 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hirahara K, Kano Y, Sato Y, Horie C, Okazaki A, Ishida T, et al.Methylprednisolone pulse therapy for Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis: clinical evaluation and analysis of biomarkers. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2013;69(3):496-8. - PubMed
Journet 1980 {published data only}
-
- Journet M.Treatment of polymorph erythema and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Union Medicale du Canada 1980;109(10):1494-5. - PubMed
Kaushik 2019 {published data only}
-
- Kaushik A, Kumaran MS, Vinay K, Mehta S, Singh P.Cyclosporine-induced toxic leukoencephalopathy in toxic epidermal necrolysis. International Journal of Dermatology 2019;58(2):e36-8. - PubMed
Khapii 1987 {published data only}
-
- Khapii KK, Kulikova LP, Kil'diushevskii AV.Plasmapheresis in the combined therapy of Lyell's syndrome. Anesteziologiia I Reanimatologiia 1987;2:61-2. - PubMed
Kim 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kim KJ, Jee MS, Han MH, Choi JH, Sung KJ, Moon KC, et al.The effect of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis. Korean Journal of Dermatology 2002;40(7):766-71.
Krajewski 2019 {published data only}
-
- Krajewski A, Mazurek MJ, Mlynska-Krajewska E, Piorun K, Knakiewicz M, Markowska M.Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis therapy with TPE and IVIG-10 years of experience of the Burns Treatment Center. Journal of Burn Care & Research 2019;40(5):652-7. - PubMed
Lalevee 2018 {published data only}
-
- Lalevee S, Audureau E, Riou A, Colin A, Anquetin M, Barau C, et al.Cytokine profile in 133 patients with severe cutaneous adverse reactions. Clinical and Translational Allergy 2018;8(Suppl 3):P01.
Lalosevic 2015 {published data only}
-
- Lalosevic J, Nikolic M, Gajic-Veljic M, Skiljevic D, Medenica L.Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a 20-year single-center experience. International Journal of Dermatology 2015;54(8):978-84. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Mockenhaupt 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mockenhaupt M, Schlingmann J, Schopf E.Immunomodulating therapy in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. H+G Zeitschrift fur Hautkrankheiten 2000;75(7-8):467.
Morgado‐Carrasco 2019 {published data only}
Mori 2019 {published data only}
-
- Mori F, Liccioli G, Parronchi P, Barni S, Capone M, Sarti L, et al.Aetiopathogenesis of severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARS) in children: a 9-year experience in a tertiary-care paediatric hospital setting. Allergy: European Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2019;74(Suppl 106):30. - PubMed
NCT02037347 {published data only}
-
- NCT02037347.Study to evaluate the use of palifermin to treat toxic epidermal necrolysis. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02037347 (first received 15 January 2014).
Nixon 1985 {published data only}
Noe 2018 {published data only}
-
- Noe MH, Mostaghimi A, Rosenbach M, Shinkai K, Micheletti RG.Selective use of cyclosporine for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis may exclude patients with poor prognostic factors. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2018;138(9):2068-72. - PubMed
Paquet 2006 {published data only}
-
- Paquet P, Kaveri S, Jacob E, Pirson J, Quatresooz P, Pierard GE.Skin immunoglobulin deposition following intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Experimental Dermatology 2006;15(5):381-6. - PubMed
Patterson 1992 {published data only}
-
- Patterson R, Grammer LC, Greenberger PA, Lawrence ID, Zeiss CR, Detjen PF, et al.Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS): effectiveness of corticosteroids in management and recurrent SJS. Allergy and Asthma Proceedings 1992;13(2):89-95. - PubMed
Pham 2020 {published data only}
Pisani 1981 {published data only}
-
- Pisani M, Ruocco V.Beneficial effect of hyperbaric oxygen on toxic epidermal necrolysis and pemphigus vulgaris. Annali Italiani di Dermatologia Clinica e Sperirentale 1981;35(4):581-4.
Revuz 1978 {published data only}
-
- Revuz J, Laroche L, Touraine R.The treatment of acute epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome). The contribution of two recent techniques [Traitement de la nécrolyse épidermique aiguë (Syndrome de Lyell). Apport de deux techniques récentes]. La Nouvelle Presse Medicale 1978;7(47):4273-6. - PubMed
Sasidharanpillai 2015 {published data only}
Shah 2019 {published data only}
-
- Shah R, Chen ST, Kroshinsky D.Use of cyclosporine for the treatment of Steven Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2019;85(2):512-513. - PubMed
Stella 2001 {published data only}
-
- Stella M, Cassano P, Bollero D, Clemente A, Giorio G.Toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with intravenous high-dose immunoglobulins: our experience. Dermatology 2001;203(1):45-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sudusinghe 2018 {published data only}
-
- Sudusinghe H, Pirabakaran S, Nanayakkara K, Seneviratne J, Samaraweera S.Patterned behaviour and response to current treatments among children with Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis spectrum: a prospective study. Australian Journal of Dermatology 2018;59(Suppl 1):16-7.
Tao 2013 {published data only}
-
- Tao Y, Wang Y, Ye L.Clinical efficacy of hemoperfusion in 10 children with severe drug eruption. Pediatric Nephrology 2013;28(8):1674.
Trautmann 1998 {published data only}
-
- Trautmann A, Klein CE, Kampgen E, Brocker EB.Severe bullous drug reactions treated successfully with cyclophosphamide. British Journal of Dermatology 1998;139(6):1127-8. - PubMed
Viard 1998 {published data only}
-
- Viard I, Wehrli P, Bullani R, Schneider P, Holler N, Salomon D, et al.Inhibition of toxic epidermal necrolysis by blockade of CD95 with human intravenous immunoglobulin. Science 1998;282(5388):490-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Wolkenstein 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wolkenstein P.Thalidomide and emergent conditions. Annales de Dermatologie et de Venereologie 2002;129:WK0718.
Yeung 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yeung CK, Lam LK, Chan HH.The timing of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology: Viewpoints in Dermatology 2005;30(5):600-2. - PubMed
Zajicek 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zajicek R, Pintar D, Broz L, Suca H, Konigova R.Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome at the Prague Burn Centre 1998-2008. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2012;26(5):639-43. - PubMed
Zhang 2017 {published data only}
-
- Zhang F, Zhou J.Toxic epidermal necrolysis: 13 years of experience in the management at a Department of Dermatology in China. Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology 2017;36(1):19-24. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
ChiCTR‐TRC‐13003550 {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR-TRC-13003550.Use of glucocorticoid alone or plus intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) for the treatment of severe drug eruption. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ChiCTR-TRC-13003550 (first received 3 September 2013).
References to ongoing studies
NCT02739295 {published data only}
-
- NCT02739295.G-CSF in the treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02739295 (first received 15 April 2016).
NCT02987257 {published data only}
-
- NCT02987257.NATIENS: Optimal management and mechanisms of SJS/TEN (NATIENS). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02987257 (first received 8 December 2016).
NCT03585946 {published data only}
-
- NCT03585946.Outcomes in Stevens Johnsons Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03585946 (first received 13 July 2018).
Additional references
Arevalo 2000
-
- Arévalo JM, Lorente JA, González-Herrada C, Jiménez- Reyes J.Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis with cyclosporin A. Journal of Trauma 2000;48(3):473-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Barron 2015
-
- Barron SJ, Del Vecchio MT, Aronoff SC.Intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a meta-analysis with meta-regression of observational studies. International Journal of Dermatology 2015;54(1):108-15. - PubMed
Bastuji‐Garin 1993
-
- Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, Shear NH, Naldi L, Roujeau JC.Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme. Archives of Dermatology 1993;129(1):92-6. - PubMed
Bastuji‐Garin 2000
-
- Bastuji-Garin S, Fouchard N, Bertocchi M, Roujeau JC, Revuz J, Wolkenstein P.SCORTEN: a severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2000;115(2):149-53. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Campione 2003
-
- Campione E, Marulli GC, Carrozzo AM, Chimenti MS, Costanzo A, Bianchi L.High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin for severe drug reactions: efficacy in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2003;83(6):430-2. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Chave 2005
-
- Chave TA, Mortimer NJ, Sladden MJ, Hall AP, Hutchinson PE.Toxic epidermal necrolysis: current evidence, practical management and future directions. British Journal of Dermatology 2005;153(2):241-53. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Cheung 2013
-
- Cheung YK, Cheng SH, Chan EJ, Lo SV, Ng MH, Kwan P.HLA-B alleles associated with severe cutaneous reactions to antiepileptic drugs in Han Chinese. Epilepsia 2013;54(7):1307-14. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Chung 2004
-
- Chung WH, Hung SI, Hong HS, Hsih MS, Yang LC, Ho HC, et al.Medical genetics: a marker for Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Nature 2004;428(6982):486. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Covidence [Computer program]
-
- Covidence.Version accessed 5 June 2018. Melbourne, Australia: Veritas Health Innovation, 2018. Available at covidence.org.
Deeks 2022
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG.Chapter 10. Analyzing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
de Sica‐Chapman 2010
-
- Sica-Chapman A, Williams G, Soni N, Bunker CB.Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Chelsea & Westminster TEN management protocol [corrected]. British Journal of Dermatology 2010;162(4):860-5. - PubMed
Dietrich 1995
-
- Dietrich A, Kawakubo Y, Rzany B, Mockenhaupt M, Simon JC, Schöpf E.Low N-acetylating capacity in patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Experimental Dermatology 1995;4(5):313-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Dijkers 2013
-
- Dijkers M.Introducing GRADE: a systematic approach to rating evidence in systematic reviews and to guideline development. ktdrr.org/products/update/v1n5/dijkers_grade_ktupdatev1n5.pdf (accessed prior to 5 June 2018).
Dodiuk‐Gad 2015
-
- Dodiuk-Gad RP, Olteanu C, Jeschke MG, Cartotto R, Fish J, Shear NH.Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis in North America. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;73(5):876-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Eden 2011
-
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Standards for Systematic Reviews of Comparative Effectiveness Research.Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Checklist. In: Eden J, Levit L, Berg A, et al, editors(s). Finding What Works in Health Care: Standards for Systematic Reviews. Washington, DC: National Academies Press, 2011. - PubMed
Eldridge 2020
-
- Eldridge S, Campbell MK, Campbell MJ, Drahota AK, Giraudeau B, Reeves BC, et al.Revised Cochrane risk of bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2). Additional considerations for cluster-randomized trials (RoB 2 CRT). www.riskofbias.info/welcome/rob-2-0-tool/rob-2-for-cluster-randomized-tr... (accessed 20 January 2021).
Famularo 2007
-
- Famularo G, DiDona B, Canzona F, Girardelli CR, Cruciani G.Etanercept for toxic epidermal necrolysis. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2007;41(6):1083-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Faye 2005
-
- Faye O, Roujeau JC.Treatment of epidermal necrolysis with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins (IV Ig): clinical experience to date. Drugs 2005;65(15):2085-90. [PMID: ] - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- GRADEpro GDT.Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), accessed 5 June 2018. Available at gradepro.org.
Gubinelli 2009
-
- Gubinelli E, Canzona F, Tonanzi T, Raskovic D, Didona B.Toxic epidermal necrolysis successfully treated with etanercept. Journal of Dermatology 2009;36(3):150-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hall 1992
-
- Hall AG, Tilby MJ.Mechanisms of action of, and modes of resistance to, alkylating agents used in the treatment of haematological malignancies. Blood Reviews 1992;6(3):163-73. - PubMed
Hasan 2020
Higgins 2021a
-
- Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors).Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.2 (updated February 2021). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2021. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2021b
-
- Higgins JPT, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Sterne JAC.Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.2 (updated February 2021). Cochrane, 2021. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Higgins 2021c
-
- Higgins JPT, Eldridge S, Li T.Chapter 23: Including variants on randomized trials. In: Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.2 (updated February 2021). Cochrane, 2021. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Hoffman 2021
Hsu 2016
-
- Hsu DY, Brieva J, Silverberg NB, Silverberg JI.Morbidity and mortality of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in United States adults. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2016;136(7):1387-97. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hung 2005
Jarrett 1997
-
- Jarrett P, Rademaker M, Havill J, Pullon H.Toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with cyclosporin and granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 1997;22(3):146-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kirchhof 2014
-
- Kirchhof MG, Miliszewski MA, Sikora S, Papp A, Dutz JP.Retrospective review of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis treatment comparing intravenous immunoglobulin with cyclosporine. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014;71(5):941-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Klausner 1996
-
- Klausner JD, Freedman VH, Kaplan G .Thalidomide as an anti-TNF-α inhibitor: implications for clinical use. Clinical Immunology and Immunopathology 1996;81:219-23. - PubMed
Kohanim 2016
-
- Kohanim S, Palioura S, Saeed HN, Akpek EK, Amescua G, Basu S, et al.Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis – a comprehensive review and guide to therapy. I. Systemic disease. Ocular Surface 2016;14(1):2-19. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lalosevic 2015
-
- Lalosevic J, Nikolic M, Gajic-Veljic M, Skiljevic D, Medenica L.Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a 20-year single-center experience. International Journal of Dermatology 2015;54(8):978-84. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Law 2015
-
- Law EH, Leung M.Corticosteroids in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis: current evidence and implications for future research. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2015;49(3):335-42. - PubMed
Lawless 1986
-
- Lawless JF.Regression methods for Poisson process data. Journal of the American Statistical Association 1986;82(399):808-15. [DOI: 10.2307/2288790] - DOI
Mahar 2014
-
- Mahar PD, Wasiak J, Hii B, Cleland H, Watters DA, Gin D, et al.A systematic review of the management and outcome of toxic epidermal necrolysis treated in burns centres. Burns 2014;40(7):1245-54. - PubMed
McCormack 2011
McGuinness 2020
Napolitano 2013
-
- Napolitano M, Giampetruzzi AR, Didona D, Papi M, Didona B.Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus successfully treated with a single dose of etanercept: report of three cases. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2013;69(6):E303-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Nickoloff 2008
-
- Nickoloff BJ.Saving the skin from drug-induced detachment. Nature Medicine 2008;14(12):1311-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Page 2022
-
- Page MJ, Higgins JPT, Sterne JAC.Chapter 13. Assessing risk of bias due to missing results in a synthesis. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane, 2022. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Paradisi 2014
-
- Paradisi A, Abeni D, Bergamo F, Ricci F, Didona D, Didona B.Etanercept therapy for toxic epidermal necrolysis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014;71(2):278-83. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Patel 2013
-
- Patel TK, Barvaliya MJ, Sharma D, Tripathi C.A systematic review of the drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Indian population. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology 2013;79(3):389-98. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Patmanidis 2012
-
- Patmanidis K, Sidiras A, Dolianitis K, Simelidis D, Solomonidis C, Gaitanis G, et al.Combination of infliximab and high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin for toxic epidermal necrolysis: successful treatment of an elderly patient. Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine 2012;2012:915314. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Poizeau 2018
-
- Poizeau F, Gaudin O, Le Cleach L, Duong TA, Hua C, Hotz C, et al.Ciclosporine for epidermal necrolysis: absence of beneficial effect in a retrospective cohort of 174 patients - exposed/unexposed and propensity-score matched analyses. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2018;138(6):1293-300. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Prins 2003
-
- Prins C, Kerdel FA, Padilla RS, Hunziker T, Chimenti S, Viard I, et al.Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins: multicenter retrospective analysis of 48 consecutive cases. Archives of Dermatology 2003;139(1):26-32. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Rai 2008
-
- Rai R, Srinivas CR.Suprapharmacologic doses of intravenous dexamethasone followed by cyclosporine in the treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology 2008;74(3):263-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Reese 2011
-
- Reese D, Henning JS, Rockers K, Ladd D, Gilson R.Cyclosporine for SJS/TEN: a case series and review of the literature. Cutis 2011;87(1):24-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Review Manager 2020 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5).Version 5.4. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020.
RevMan Web 2020 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager Web (RevMan Web).Version 1.22.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020. Available at revman.cochrane.org.
Revuz 1987
-
- Revuz J, Penso D, Roujeau JC, Guillaume JC, Payne CR, Wechsler J, et al.Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Clinical findings and prognosis factors in 87 patients. Archives of Dermatology 1987;123(9):1160-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Robak 2001
-
- Robak E, Robak T, Góra-Tybor J, Chojnowski K, Strzelecka B, Waszczykowska E, et al.Toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient with severe aplastic anemia treated with cyclosporin A and G-CSF. Journal of Medicine 2001;32(1-2):31-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Romanelli 2008
-
- Romanelli P, Schlam E, Green JB, Trent JT, Ricotti C, Elgart GW, et al.Immunohistochemical evaluation of toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with human intravenous immunoglobulin. Giornale Italiano di Dermatologia e Venereologia 2008;143(4):229-33. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Roujeau 1995
-
- Roujeau JC, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Rzany B, Stern RS, Anderson T, et al.Medication use and the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. New England Journal of Medicine 1995;333(24):1600-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sachdeva 2021
-
- Sachdeva M, Mufti A, Kim P, Maliyar K, Sibbald C.Biologic treatment in pediatric Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis: a systematic review. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2021;85(4):1011-3. - PubMed
Schunemann 2022a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Skoetz N, Guyatt GH.Chapter 14. Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the confidence in or quality of the evidence. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane, 2022. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Schunemann 2022b
-
- Schunemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al.Chapter 15. Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane, 2022. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Scott‐Lang 2014
-
- Scott-Lang V, Tidman M, McKay D.Toxic epidermal necrolysis in a child successfully treated with infliximab. Pediatric Dermatology 2014;31(4):532-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sekula 2013
-
- Sekula P, Dunant A, Mockenhaupt M, Naldi L, Bouwes Bavinck JN, Halevy S, et al.Comprehensive survival analysis of a cohort of patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2013;133(5):1197-204. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Singh 2013
-
- Singh GK, Chatterjee M, Verma R.Cyclosporine in Stevens Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis and retrospective comparison with systemic corticosteroid. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology 2013;79(5):686-92. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Stella 2001
-
- Stella M, Cassano P, Bollero D, Clemente A, Giorio G.Toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with intravenous high dose immunoglobulins: our experience. Dermatology 2001;203(1):45-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sterne 2016
Sterne 2019
-
- Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al.RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019;366:l4898. - PubMed
Su 2017
-
- Su S-C, Mockenhaupt M, Wolkenstein P, Dunant A, Le Gouvello S, Chen C-B, et al.Interleukin-15 is associated with severity and mortality in Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2017;137(5):1065-73. - PubMed
Sullivan 1996
-
- Sullivan JR, Watson A.Lamotrigine-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with intravenous cyclosporin: a discussion of pathogenesis and immunosuppressive management. Australian Journal of Dermatology 1996;37(4):208-12. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Trent 2008
-
- Trent JT, Kirsner RS, Romanelli P, Kerdel FA.Analysis of intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis using SCORTEN: the University of Miami experience. Archives of Dermatology 2008;139(1):39-43. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Tristani‐Firouzi 2002
-
- Tristani-Firouzi P, Petersen MJ, Saffle JR, Morris SE, Zone JJ.Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis with intravenous immunoglobulin in children. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2002;47(4):548-52. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Tsai 2021
-
- Tsai TY, Huang IH, Chao YC, Li H, Hsieh TS, Wang HH, et al.Treating toxic epidermal necrolysis with systemic immunomodulating therapies: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2021;84(2):390-7. - PubMed
Valeyrie‐Allanore 2010
-
- Valeyrie-Allanore L, Wolkenstein P, Brochard L, Ortonne N, Maître B, Revuz J, et al.Open trial of ciclosporin treatment for Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. British Journal of Dermatology 2010;163(4):847-53. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Viard 1998
-
- Viard I, Wehrli P, Bullani R, Schneider P, Holler N, Salomon D, et al.Inhibition of toxic epidermal necrolysis by blockade of CD95 with human intravenous immunoglobulin. Science 1998;282(5388):490-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
White 2018
Wojtkiewicz 2008
-
- Wojtkiewicz A, Wysocki M, Fortuna J, Chrupek M, Matczuk M, Koltan A, et al.Beneficial and rapid effect of infliximab on the course of toxic epidermal necrolysis. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2008;88(4):420-1. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Yamane 2016
-
- Yamane Y, Matsukura S, Watanabe Y, Yamaguchi Y, Nakamura K, Kambara T, et al.Retrospective analysis of Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in 87 Japanese patients. Allergy International 2016;65(1):74-81. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Yang 2016
Zaki 1995
-
- Zaki I, Patel S, Reed R, Dalziel KL.Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with severe hypocalcaemia, and treated with cyclosporin. British Journal of Dermatology 1995;133(2):337-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Zarate‐Correa 2013
-
- Zárate-Correa LC, Carrillo-Gómez DC, Ramírez-Escobar AF, Serrano-Reyes C.Toxic epidermal necrolysis successfully treated with infliximab. Journal of Investigational Allergology & Clinical Immunology 2013;23(1):61-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Langley 2018
-
- Langley A, Worley B, Pardo Pardo J, Beecker J, Ramsay T, Saavedra A, et al.Systemic interventions for treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS/TEN overlap syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, Issue 9. Art. No: CD013130. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013130] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

