Hydrazone and Oxime Olefination via Ruthenium Alkylidenes
- PMID: 35275430
- PMCID: PMC9117432
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202112101
Hydrazone and Oxime Olefination via Ruthenium Alkylidenes
Abstract
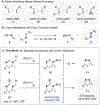
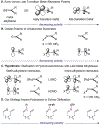
We describe the development of an efficient method for the olefination of hydrazones and oximes. The key design approach that enables this transformation is tuning of the energy/polarity of C=N π-bonds by employing heteroatom functionalities (NR2 , OR). The resulting hydrazones or oximes facilitate olefination with ruthenium alkylidenes. Through this approach, we show that air-stable, commercially available ruthenium alkylidenes provide access to functionalized alkenes (20 examples) in ring-closing reactions with yields up to 88 %.
Keywords: Alkylidenes; Hydrazones; Olefination; Oximes; Ruthenium.
© 2022 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lysenko Z, Maughon BR, Bicerano J, Burdett KA, Christenson CP, Cummins CH, Dettloff ML, Schrock AK, Thomas PJ, Varjian RD, White JE, Maher JM, Integrated Chemical Processes for Industrial Utilization of Seed Oils, 2010, US7745652B2.
-
- Obrecht W, Müller JM, Nuyken O, Kellner M, Process for the Metathetic Degradation of Nitrile Rubbers, 2010, US7662889B2.
-
- Davidson MH, Robinson JG, Expert Opin. Pharmacother 2006, 7, 1701–1714. - PubMed
-
- Kidd J, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2006, 5, 813–814. - PubMed
-
- LoRusso PM, Weiss D, Guardino E, Girish S, Sliwkowski MX, Clin Cancer Res 2011, 17, 6437–6447. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

