Yoga Prevents Gray Matter Atrophy in Women at Risk for Alzheimer's Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35275541
- PMCID: PMC9198760
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-215563
Yoga Prevents Gray Matter Atrophy in Women at Risk for Alzheimer's Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Female sex, subjective cognitive decline (SCD), and cardiovascular risk factors (CVRFs) are known risk factors for developing Alzheimer's disease (AD). We previously demonstrated that yoga improved depression, resilience, memory and executive functions, increased hippocampal choline concentrations, and modulated brain connectivity in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Objective: In this study (NCT03503669), we investigated brain gray matter volume (GMV) changes in older women with SCD and CVRFs following three months of yoga compared to memory enhancement training (MET).
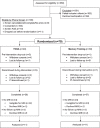
Methods: Eleven women (mean age = 61.45, SD = 6.58) with CVRF and SCD completed twelve weeks of Kundalini Yoga and Kirtan Kriya (KY + KK) while eleven women (mean age = 64.55, SD = 6.41) underwent MET. Anxiety, resilience, stress, and depression were assessed at baseline and 12 weeks, as were T1-weighted MRI scans (Siemens 3T Prisma scanner). We used Freesurfer 6.0 and tested group differences in GMV change, applying Monte-Carlo simulations with alpha = 0.05. Region-of-interest analysis was performed for hippocampus and amygdala.
Results: Compared to KY + KK, MET showed reductions in GMV in left prefrontal, pre- and post-central, supramarginal, superior temporal and pericalcarine cortices, right paracentral, postcentral, superior and inferior parietal cortices, the banks of the superior temporal sulcus, and the pars opercularis. Right hippocampal volume increased after yoga but did not survive corrections.
Conclusion: Yoga training may offer neuroprotective effects compared to MET in preventing neurodegenerative changes and cognitive decline, even over short time intervals. Future analyses will address changes in functional connectivity in both groups.
Keywords: Brain; Kirtan Kriya; Kundalini; MRI; cardiovascular risk; gray matter; memory; memory training; mind-body; prevention; women; yoga.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures available online (
Figures

References
-
- Prince M, Bryce R, Albanese E, Wimo A, Ribeiro W, Ferri CP (2013) The global prevalence of dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimers Dement 9, 63–75.e62. - PubMed
-
- Snyder HM, Shineman DW, Friedman LG, Hendrix JA, Khachaturian A, Le Guillou I, Pickett J, Refolo L, Sancho RM, Ridley SH (2016) Guidelines to improve animal study design and reproducibility for Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias: For funders and researchers. Alzheimers Dement 12, 1177–1185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

