Hospitalization costs of coronaviruses diseases in upper-middle-income countries: A systematic review
- PMID: 35275935
- PMCID: PMC8916657
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265003
Hospitalization costs of coronaviruses diseases in upper-middle-income countries: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: COVID-19, SARS and MERS are diseases that present an important health burden worldwide. This situation demands resource allocation to the healthcare system, affecting especially middle- and low-income countries. Thus, identifying the main cost drivers is relevant to optimize patient care and resource allocation.
Objective: To systematically identify and summarize the current status of knowledge on direct medical hospitalization costs of SARS, MERS, or COVID-19 in Upper-Middle-Income Countries.
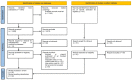
Methods: We conducted a systematic review across seven key databases (PubMed, EMBASE, BVS Portal, CINAHL, CRD library, MedRxiv and Research Square) from database inception to February 2021. Costs extracted were converted into 2021 International Dollars using the Purchasing Power Parity-adjusted. The assessment of quality was based on the protocol by the BMJ and CHEERS. PROSPERO 2020: CRD42020225757.
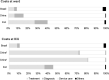
Results: No eligible study about SARS or MERS was recovered. For COVID-19, five studies presented cost analysis performed in Brazil, China, Iran, and Turkey. Regarding total direct medical costs, the lowest cost per patient at ward was observed in Turkey ($900.08), while the highest in Brazil ($5,093.38). At ICU, the lowest was in Turkey ($2,984.78), while the highest was in China ($52,432.87). Service care was the most expressive (58% to 88%) cost driver of COVID-19 patients at ward. At ICU, there was no consensus between service care (54% to 87%) and treatment (72% to 81%) as key burdens of total cost.
Conclusion: Our findings elucidate the importance of COVID-19 on health-economic outcomes. The marked heterogeneity among studies leaded to substantially different results and made challenging the comparison of data to estimate pooled results for single countries or regions. Further studies concerning cost estimates from standardized analysis may provide clearer data for a more substantial analysis. This may help care providers and policy makers to organize care for patients in the most efficient way.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jun 7];Available from: https://covid19.who.int/.
-
- Chaiyakunapruk N, Kotirum S, Newall AT, Lambach P, Hutubessy RCW. Rationale and opportunities in estimating the economic burden of seasonal influenza across countries using a standardized WHO tool and manual. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2018. Jan;12(1):13–21. doi: 10.1111/irv.12491 Epub 2017 Nov 16. . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

