Validating Accuracy of a Mobile Application against Food Frequency Questionnaire on Key Nutrients with Modern Diets for mHealth Era
- PMID: 35276892
- PMCID: PMC8839756
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14030537
Validating Accuracy of a Mobile Application against Food Frequency Questionnaire on Key Nutrients with Modern Diets for mHealth Era
Abstract
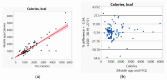
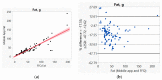
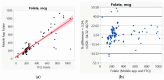
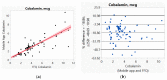
In preparation for personalized nutrition, an accurate assessment of dietary intakes on key essential nutrients using smartphones can help promote health and reduce health risks across vulnerable populations. We, therefore, validated the accuracy of a mobile application (app) against Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) using artificial intelligence (AI) machine-learning-based analytics, assessing key macro- and micro-nutrients across various modern diets. We first used Bland and Altman analysis to identify and visualize the differences between the two measures. We then applied AI-based analytics to enhance prediction accuracy, including generalized regression to identify factors that contributed to the differences between the two measures. The mobile app underestimated most macro- and micro-nutrients compared to FFQ (ranges: -5% for total calories, -19% for cobalamin, -33% for vitamin E). The average correlations between the two measures were 0.87 for macro-nutrients and 0.84 for micro-nutrients. Factors that contributed to the differences between the two measures using total calories as an example, included caloric range (1000-2000 versus others), carbohydrate, and protein; for cobalamin, included caloric range, protein, and Chinese diet. Future studies are needed to validate actual intakes and reporting of various diets, and to examine the accuracy of mobile App. Thus, a mobile app can be used to support personalized nutrition in the mHealth era, considering adjustments with sources that could contribute to the inaccurate estimates of nutrients.
Keywords: Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ); agreement and bias; dietary record; generalized regression; mHealth; mobile applications (mobile app); modern diets; personalized nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Cappuccilli M., Bergamini C., Giacomelli F.A., Cianciolo G., Donati G., Conte D., Natali T., La Manna G., Capelli I. Vitamin B Supplementation and Nutritional Intake of Methyl Donors in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Critical Review of the Impact on Epigenetic Machinery. Nutrients. 2020;12:1234. doi: 10.3390/nu12051234. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

