Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health
- PMID: 35276989
- PMCID: PMC8839325
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14030631
Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health
Abstract
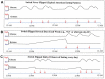
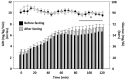
Given the ongoing strain that the obesity epidemic has placed on public health outcomes, new and effective approaches to weight control are needed. One approach to improving weight and metabolic outcomes is intermittent fasting, which consists of multiple different timing schedules for temporary food avoidance, including alternate-day fasting, other similar full-day fasting patterns, and time-restricted feeding (where the day's food is consumed over a 6-h period, allowing for 18 h of fasting). These feeding schedules have favorable metabolic effects by intermittently inducing the metabolism of fatty acids to ketones. The regimens overall lead to a decrease in weight and have been linked to improvements in dyslipidemia and blood pressure. While more research is needed on longer-term outcomes and this approach should be avoided in particular health conditions, intermittent fasting should be considered as an option for individuals who have a pattern of unhealthy weight gain using standard eating patterns.
Keywords: intermittent fasting; ketones; metabolic syndrome; obesity; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

