A Four-Probiotics Regimen Combined with A Standard Helicobacter pylori-Eradication Treatment Reduces Side Effects and Increases Eradication Rates
- PMID: 35276991
- PMCID: PMC8838490
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14030632
A Four-Probiotics Regimen Combined with A Standard Helicobacter pylori-Eradication Treatment Reduces Side Effects and Increases Eradication Rates
Abstract
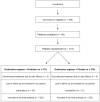
Aim: To establish whether the addition of probiotics to a globally accepted Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-eradication scheme may reduce the rates of side effects and increase the eradication rates. Methods. Prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of patients receiving eradication therapy for H. pylori in the eight participating centers. All patients received a 10-day proton pump inhibitor containing non-bismuth quadruple therapeutic regimen for H. pylori eradication (omeprazole 20 mg, amoxycillin 1 g, clarithromycin 500 mg, and metronidazole 500 mg all twice daily orally) and were randomized to receive either probiotics (group A) or placebo (group B). The probiotic used combined four probiotic strains, i.e., Lactobacillus Acidophilus, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, Bifidobacterium lactis, and Saccharomyces boulardii. Results. Data were analyzed for 329 patients in group A and 335 patients in group B. Fifty six (17.0%) patients in group A and 170 (50.7%) patients in group B reported the occurrence of an H. pylori treatment-associated new symptom or the aggravation of a pre-existing symptom of any severity (p < 0.00001). H. pylori was successfully eradicated in 303 patients in group A (92.0%) and 291 patients in group B (86.8%), (p = 0.028). Conclusion: Adding probiotics to the 10-day concomitant non-bismuth quadruple H. pylori eradication regimen increases the eradication rate and decreases side effects.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; non-bismuth quadruple eradication regimen; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Georgopoulos S.D., Xirouchakis E., Martinez-Gonzalez B., Sgouras D.N., Spiliadi C., Mentis A.F., Laoudi F. Clinical evaluation of a ten-day regimen with esomeprazole, metronidazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori in a high clarithromycin resistance area. Helicobacter. 2013;18:459–467. doi: 10.1111/hel.12062. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hill C., Guarner F., Reid G., Gibson G.R., Merenstein D.J., Pot B., Morelli L., Canani R.B., Flint H.J., Salminen S., et al. Expert Consensus document. The International Scientific Association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014;11:506–514. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical